ClickHouse datasource plugin provides a support for ClickHouse as a backend database.
Grafana team currently doesn't provide worked signing method for community plugins https://community.grafana.com/t/how-to-create-a-signed-backend-plugin/30068/2
so, for properly setup you need change configuration option
[plugins]
allow_loading_unsigned_plugins=vertamedia-clickhouse-datasource
or setup environment variable
GF_PLUGINS_ALLOW_LOADING_UNSIGNED_PLUGINS=vertamedia-clickhouse-datasource
You can install plugin from grafana.net
OR
Copy files to your Grafana plugin directory. Restart Grafana, check data sources list at http://your.grafana.instance/datasources/new, choose ClickHouse option.
- Access to CH via HTTP
- Query setup
- Raw SQL editor
- Query formatting
- Macros support
- Additional functions
- Templates
- Table view
- SingleStat view
- Ad-hoc filters
- Annotations
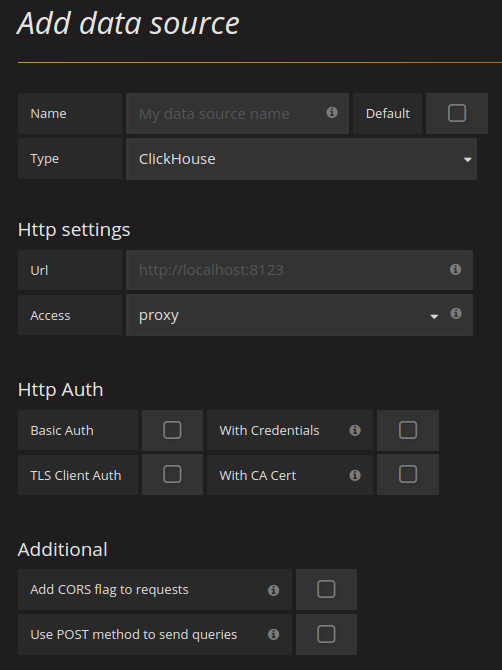
Page configuration is standard
There is a small feature - ClickHouse treats HTTP Basic Authentication credentials as a database user and will try to run queries using its name.
CHProxy (optional)
Using of CHProxy will bring additional features:
- Easily setup
HTTPSaccess to ClickHouse as shown here to provide secure access. - Limit concurrency and execution time for requests from
Grafanaas shown here to preventClickHouseoverloading fromGrafana. - Protection against request bursts for dashboards with numerous graphs.
CHProxyallows queueing requests and execute them sequentially. To learn more - read about paramsmax_queue_sizeandmax_queue_timeat CHProxy page. - Response caching for the most frequent queries as shown here.
Cachingwill protectClickHousefrom excessive refreshes and will be optimal option for popular dashboards.
Hint - if you need to cache requests like
last 24hwhere timestamp changes constantly then try to useRoundoption atRaw Editor
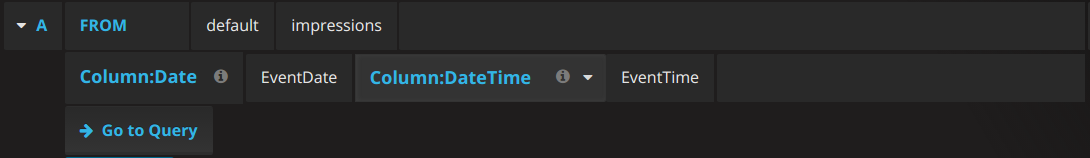
Query setup interface:
First row FROM contains two options: database and table. Table values depends on a selected database.
Second row contains selectors for time filtering:
Plugin will try to detect date columns automatically
Column:DateTimeorColumn:TimeStampare required for time-based macros and functions because all analytics based on these values
Button Go to Query is just a toggler to Raw SQL Editor
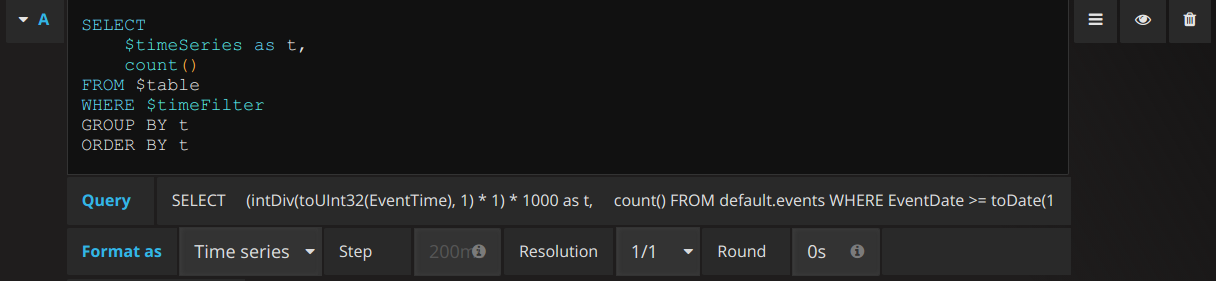
Raw Editor allows custom SQL queries to be written:
Raw Editor allows typing queries, get info about functions and macros, format queries as Clickhouse do. Under the Editor you can find a raw query (all macros and functions have already been replaced) which will be sent directly to ClickHouse.
Plugin supports the following marcos:
- $table - replaced with selected table name from Query Builder
- $dateCol - replaced with
Column:Datevalue from Query Builder - $dateTimeCol - replaced with
Column:DateTimeorColumn:TimeStampvalue from Query Builder - $from - replaced with (timestamp with ms)/1000 value of UI selected "Time Range:From"
- $to - replaced with (timestamp with ms)/1000 value of UI selected "Time Range:To"
- $interval - replaced with selected "Group by a time interval" value (as a number of seconds)
- $timeFilter - replaced with currently selected "Time Range". Requires Column:Date and Column:DateTime or Column:TimeStamp to be selected.
- $timeFilterByColumn($column) - replaced with currently selected "Time Range" for a column passed as
$columnargument. Use it in queries or query variables as...WHERE $timeFilterColumn($column)...or...WHERE $timeFilterColumn(created_at).... - $timeSeries - replaced with special ClickHouse construction to convert results as time-series data. Use it as "SELECT $timeSeries...".
- $unescape - unescapes variable value by removing single quotes. Used for multiple-value string variables: "SELECT $unescape($column) FROM requests WHERE $unescape($column) = 5"
- $adhoc - replaced with a rendered ad-hoc filter expression, or "1" if no ad-hoc filters exist. Since ad-hoc applies automatically only to outer queries the macros can be used for filtering in inner queries.
A description of macros is available by typing their names in Raw Editor
Functions are just templates of SQL queries, and you can check the final query at Raw SQL Editor mode. If you need some additional complexity - just copy raw sql into Raw Editor and make according changes. Remember that macros are still available to use.
There are some limits in function use because of poor query analysis:
- Column:Date and Column:DateTime or Column:TimeStamp must be set in Query Builder
- Query must begin from function name
- Only one function can be used per query
Plugin supports the following functions:
Example usage:
$rate(countIf(Type = 200) AS good, countIf(Type != 200) AS bad) FROM requests
Query will be transformed into:
SELECT
t,
good / runningDifference(t / 1000) AS goodRate,
bad / runningDifference(t / 1000) AS badRate
FROM
(
SELECT
(intDiv(toUInt32(EventTime), 60)) * 1000 AS t,
countIf(Type = 200) AS good,
countIf(Type != 200) AS bad
FROM requests
WHERE ((EventDate >= toDate(1482796747)) AND (EventDate <= toDate(1482853383))) AND ((EventTime >= toDateTime(1482796747)) AND (EventTime <= toDateTime(1482853383)))
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY t
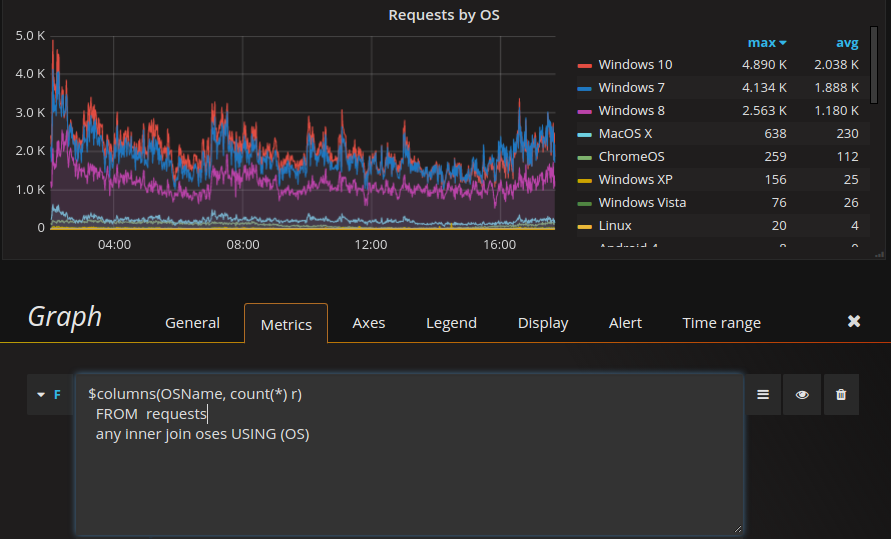
) Example usage:
$columns(OSName, count(*) c)
FROM requests
ANY INNER JOIN oses USING (OS)
Query will be transformed into:
SELECT
t,
groupArray((OSName, c)) AS groupArr
FROM
(
SELECT
(intDiv(toUInt32(EventTime), 60) * 60) * 1000 AS t,
OSName,
count(*) AS c
FROM requests
ANY INNER JOIN oses USING (OS)
WHERE ((EventDate >= toDate(1482796627)) AND (EventDate <= toDate(1482853383))) AND ((EventTime >= toDateTime(1482796627)) AND (EventTime <= toDateTime(1482853383)))
GROUP BY
t,
OSName
ORDER BY
t,
OSName
)
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY tThis will help to build the next graph:
Example usage:
$rateColumns(OS, count(*) c) FROM requests
Query will be transformed into:
SELECT
t,
arrayMap(lambda(tuple(a), (a.1, a.2 / runningDifference(t / 1000))), groupArr)
FROM
(
SELECT
t,
groupArray((OS, c)) AS groupArr
FROM
(
SELECT
(intDiv(toUInt32(EventTime), 60) * 60) * 1000 AS t,
OS,
count(*) AS c
FROM requests
WHERE ((EventDate >= toDate(1482796867)) AND (EventDate <= toDate(1482853383))) AND ((EventTime >= toDateTime(1482796867)) AND (EventTime <= toDateTime(1482853383)))
GROUP BY
t,
OS
ORDER BY
t,
OS
)
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY t
)
$perSecond(cols...) - converts query results as "change rate per interval" for Counter-like(growing only) metrics
Example usage:
$perSecond(Requests) FROM requests
Query will be transformed into:
SELECT
t,
if(runningDifference(max_0) < 0, nan, runningDifference(max_0) / runningDifference(t / 1000)) AS max_0_Rate
FROM
(
SELECT
(intDiv(toUInt32(EventTime), 60) * 60) * 1000 AS t,
max(Requests) AS max_0
FROM requests
WHERE ((EventDate >= toDate(1535711819)) AND (EventDate <= toDate(1535714715)))
AND ((EventTime >= toDateTime(1535711819)) AND (EventTime <= toDateTime(1535714715)))
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY t
)// see issue 78 for the background
$perSecondColumns(key, value) - is a combination of $columns and $perSecond for Counter-like metrics
Example usage:
$perSecondColumns(Protocol, Requests) FROM requests WHERE Protocol in ('udp','tcp')
Query will be transformed into:
SELECT
t,
groupArray((Protocol, max_0_Rate)) AS groupArr
FROM
(
SELECT
t,
Protocol,
if(runningDifference(max_0) < 0, nan, runningDifference(max_0) / runningDifference(t / 1000)) AS max_0_Rate
FROM
(
SELECT
(intDiv(toUInt32(EventTime), 60) * 60) * 1000 AS t,
Protocol,
max(Requests) AS max_0
FROM requests
WHERE ((EventDate >= toDate(1535711819)) AND (EventDate <= toDate(1535714715)))
AND ((EventTime >= toDateTime(1535711819)) AND (EventTime <= toDateTime(1535714715)))
AND (Protocol IN ('udp', 'tcp'))
GROUP BY
t,
Protocol
ORDER BY
t,
Protocol
)
)
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY t// see issue 80 for the background
If you add a template variable of the type Query, you can write a ClickHouse query that can
return things like measurement names, key names or key values that are shown as a dropdown select box.
For example, you can have a variable that contains all values for the hostname column in a table if you specify a query like this in the templating variable Query setting.
SELECT hostname FROM hostTo use time range dependent macros like timeFilterByColumn($column) in your query the refresh mode of the template variable needs to be set to On Time Range Change.
SELECT event_name FROM event_log WHERE $timeFilterByColumn(time_column)Another option is a query that can create a key/value variable. The query should return two columns that are named __text and __value. The __text column value should be unique (if it is not unique then the first value will use). The options in the dropdown will have a text and value that allows you to have a friendly name as text and an id as the value. An example query with hostname as the text and id as the value:
SELECT hostname AS __text, id AS __value FROM hostYou can also create nested variables. For example if you had another variable named region. Then you could have the hosts variable only show hosts from the current selected region with a query like this (if region is a multi-value variable then use the IN comparison operator rather than = to match against multiple values):
SELECT hostname FROM host WHERE region IN ($region)If you are using templating to feed your predicate, you will face performance degradation when everything will select as the predicate, and it's not necessary. It's also true for textbox when nothing is enter, you have to write specific sql code to handle that.
To workaround this issue a new macro $conditionalTest(SQL Predicate,$variable) can be used to remove some part of the query. If the variable is type query with all selected or if the variable is a textbox with nothing enter, then the SQL Predicate is not include in the generated query.
To give an example: with 2 variables $var query with include All option $text textbox
The following query
SELECT
$timeSeries as t,
count()
FROM $table
WHERE $timeFilter
$conditionalTest(AND toLowerCase(column) in ($var),$var)
$conditionalTest(AND toLowerCase(column2) like '%$text%',$text)
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY tif the $var is selected as "All" value, and the $text variable is empty, the query will be converted into:
SELECT
$timeSeries as t,
count()
FROM $table
WHERE $timeFilter
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY tIf the $var template variable have select some elements, and the $text template variable has at least one char, the query will be converted into:
SELECT
$timeSeries as t,
count()
FROM $table
WHERE $timeFilter
AND toLowerCase(column) in ($var)
AND toLowerCase(column2) like '%$text%'
GROUP BY t
ORDER BY tPie Chart (https://grafana.com/plugins/grafana-piechart-panel)
Remember that pie chart plugin is not welcome for using in grafana - see https://grafana.com/blog/2015/12/04/friends-dont-let-friends-abuse-pie-charts
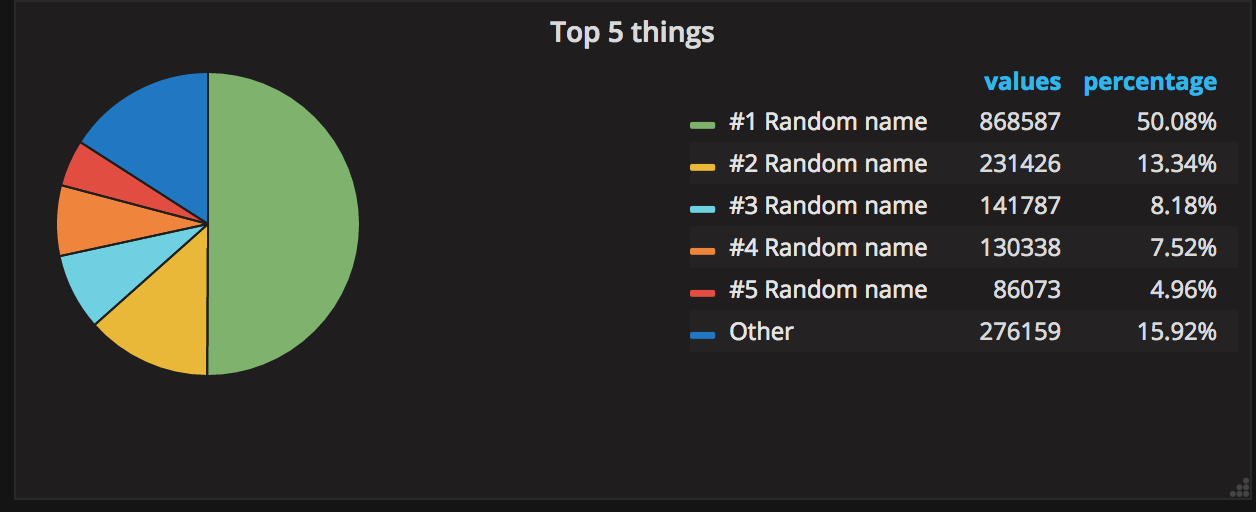
To create "Top 5" diagram we will need two queries: one for 'Top 5' rows and one for 'Other' row.
Top5:
SELECT
1 AS t, /* fake timestamp value */
UserName,
sum(Requests) AS Reqs
FROM requests
GROUP BY t, UserName
ORDER BY Reqs DESC
LIMIT 5Other:
SELECT
1 AS t, /* fake timestamp value */
UserName,
sum(Requests) AS Reqs
FROM requests
GROUP BY t, UserName
ORDER BY Reqs
LIMIT 5,10000000000000 /* select some ridiculous number after first 5 */There are don't contain any tricks in displaying time-series data. To print summary data, omit time column, and format the result as "Table".
SELECT
UserName,
sum(Requests) as Reqs
FROM requests
GROUP BY
UserName
ORDER BY
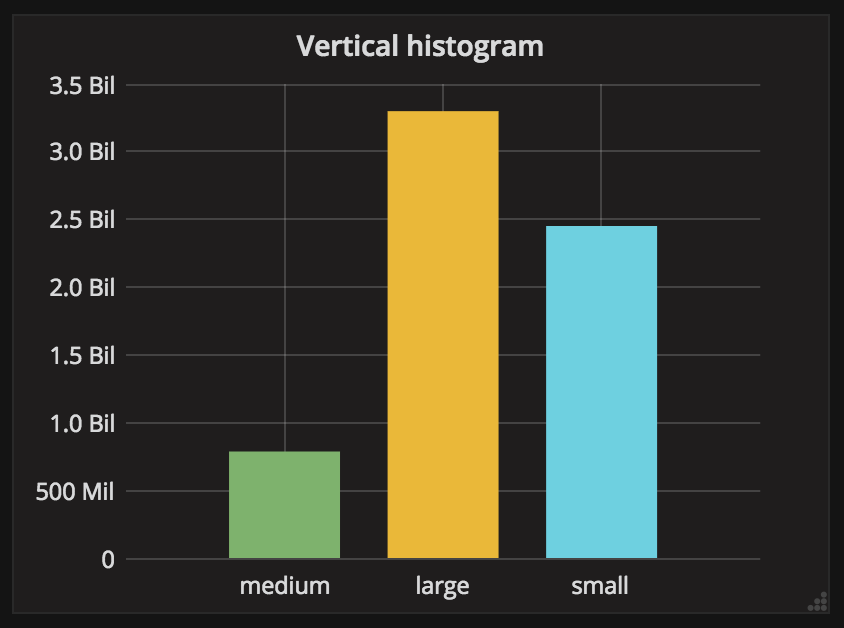
ReqsVertical histogram (https://grafana.com/plugins/graph)
To make the vertical histogram from graph panel we will need to edit some settings:
- Display -> Draw Modes -> Bars
- Axes -> X-Axis -> Mode -> Series
You can use next query:
$columns(
Size,
sum(Items) Items)
FROM some_table
// It is also possible to use query without macros
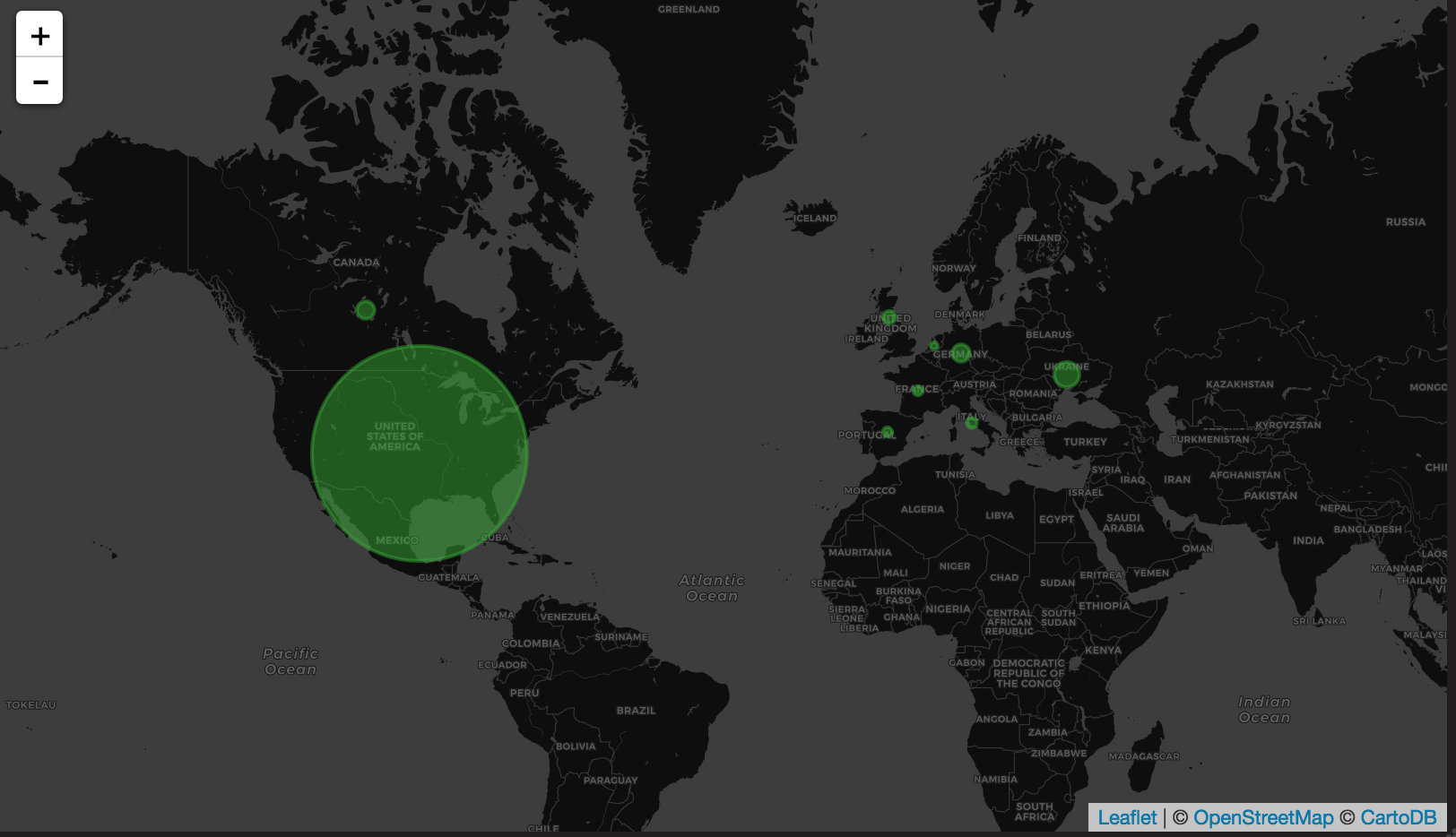
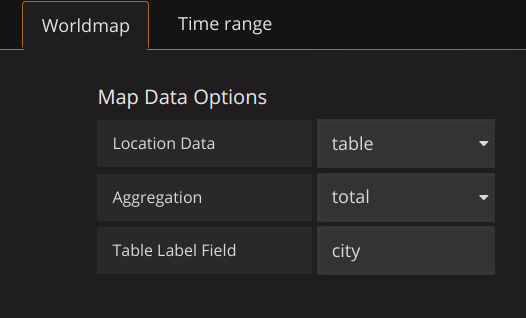
Worldmap panel (https://github.com/grafana/worldmap-panel)
If you have a table with country/city codes:
SELECT
1,
Country AS c,
sum(Requests) AS Reqs
FROM requests
GLOBAL ANY INNER JOIN
(
SELECT Country, CountryCode
FROM countries
) USING (CountryCode)
WHERE $timeFilter
GROUP BY
c
ORDER BY Reqs DESC
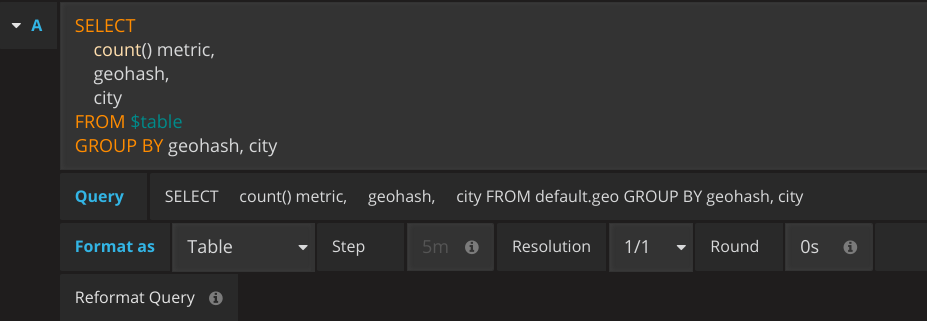
If you are using geohash set following options:
You can make following query with Table formatting:
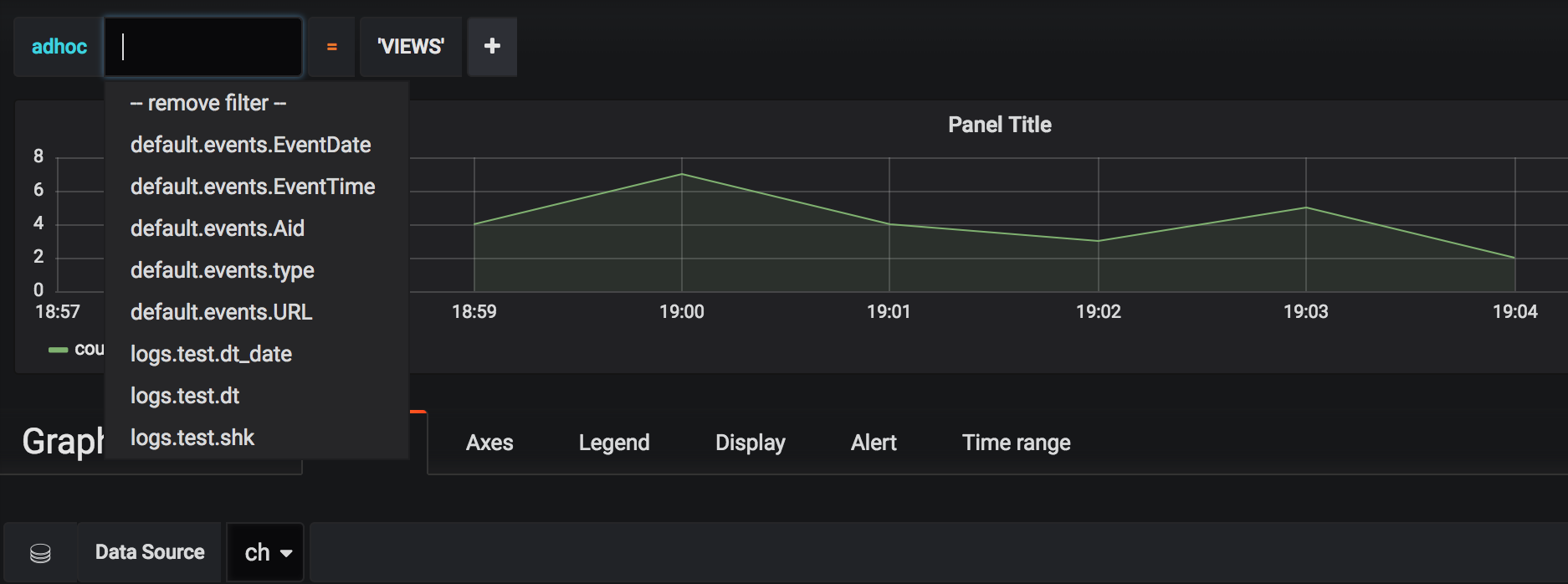
If there is an Ad-hoc variable, plugin will fetch all columns of all tables of all databases (except system database) as tags.
So in dropdown menu will be options like database.table.column. If you specify the default database it will only fetch tables and columns from that database, and the dropdown menu will have an option like table.column.
If there are ENUM columns, the plugin will fetch their options and use them as tag values.
Also, plugin will fetch 300 unique values for fields with other types.
Plugin will apply Ad-hoc filters to all queries on the dashboard if their settings $database and $table are the same
as database.table specified in Ad-hoc control. If the ad-hoc filter doesn't specify a table, it will apply to all queries regardless of the table.
This is useful if the dashboard contains queries to multiple different tables.
There are no option to apply OR operator for multiple Ad-hoc filters - see grafana/grafana#10918
There are no option to use IN operator for Ad-hoc filters due to Grafana limitations
There may be cases when CH contains too many tables and columns so their fetching could take notably amount of time. So, if you need
to have multiple dashboards with different databases using of default database won't help. The best way to solve this will be to have parametrized
ad-hoc variable in dashboard settings. Currently, it's not supported by Grafana interface (see issue).
As a temporary workaround, plugin will try to look for variable with name adhoc_query_filter and if it exists will use its value as query to fetch columns.
For this purpose we recommend creating some variable constant with the name adhoc_query_filter and set the value similar to the following one:
SELECT database, table, name, type FROM system.columns WHERE table='myTable' ORDER BY database, table
That should help to control data fetching by ad-hoc queries.
To use time range dependent macros like $from and $to in your query the refresh mode of the template variable needs to be set to On Time Range Change.
SELECT ClientID FROM events WHERE EventTime > toDateTime($from) AND EventTime < toDateTime($to)
It’s now possible to configure datasources using config files with Grafana’s provisioning system. You can read more about how it works and all the settings you can set for datasources on the provisioning docs page.
Here are some provisioning example:
apiVersion: 1
datasources:
- name: Clickhouse
type: vertamedia-clickhouse-datasource
access: proxy
url: http://localhost:8123
# <bool> enable/disable basic auth
basicAuth:
# <string> basic auth username
basicAuthUser:
# <string> basic auth password
basicAuthPassword:
# <bool> enable/disable with credentials headers
withCredentials:
# <bool> mark as default datasource. Max one per org
isDefault:
# <map> fields that will be converted to json and stored in json_data
jsonData:
# <bool> enable/disable sending 'add_http_cors_header=1' parameter
addCorsHeader:
# <bool> enable/disable using POST method for sending queries
usePOST:
# <string> default database name
defaultDatabase:
Some settings and security params are the same for all datasources. You can find them here.
Why time series last point is not the real last point?
Plugin extrapolates last datapoint if time range is last N to avoid displaying of constantly decreasing graphs
when timestamp in a table is rounded to minute or bigger.
If it so then in 99% cases last datapoint will be much less than previous one, because last minute is not finished yet.
That's why plugin checks prev datapoints and tries to predict last datapoint value just as it was already written into db.
This behavior could be turned off via "Extrapolation" checkbox in query editor.
Which table schema used in SQL query examples?
All examples in this plugin use following table schema:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS countries(
Country LowCardinality(String),
CountryCode LowCardinality(String)
) ENGINE MergeTree()
ORDER BY (CountryCode, Country);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS oses (
OSName LowCardinality(String),
OS LowCardinality(String)
) ENGINE MergeTree()
ORDER BY (OS);
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS requests(
EventTime DateTime,
EventDate Date,
Protocol LowCardinality(String),
UserName LowCardinality(String),
OS LowCardinality(String),
CountryCode LowCardinality(String),
Type UInt8,
Requests UInt32
) ENGINE=MergeTree()
ORDER BY (EventDate, EventTime, Type, OS, Protocol, UserName)
PARTITION BY toYYYYMM(EventDate);What about alerts support?
Alerts feature requires changes in Grafana's backend, which can be extended only for Grafana 6.5+. Grafana's maintainers are working on this feature.
Current alerts support for clickhouse-grafana datasource plugin in beta and support only for amd64 architecture for Linux, MacOSX, Windows.
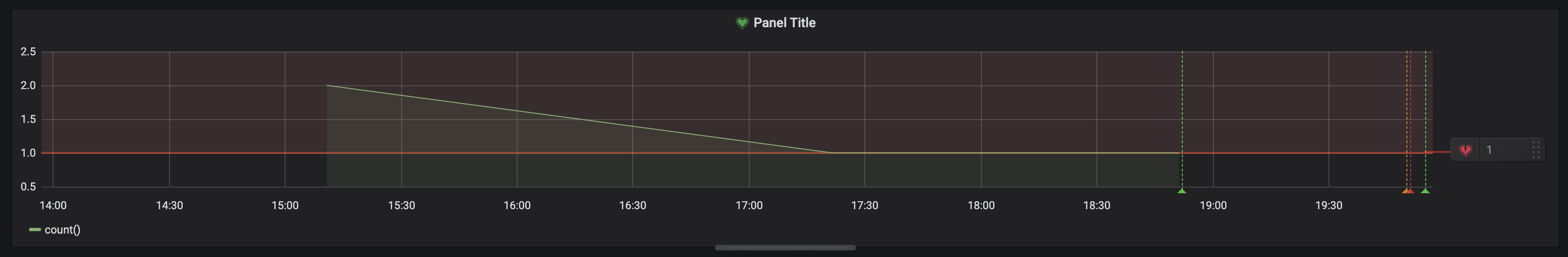
The resulting alerts should look like this
If you have any idea for an improvement or found a bug do not hesitate to open an issue or submit a pull request. We will appreciate any help from the community which will make working with such amazing products as ClickHouse and Grafana more convenient.
see CONTRIBUTING.md for Development and Pull request Contributing instructions
MIT License, please see LICENSE for details.