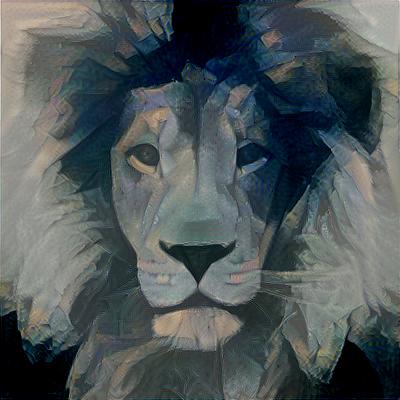
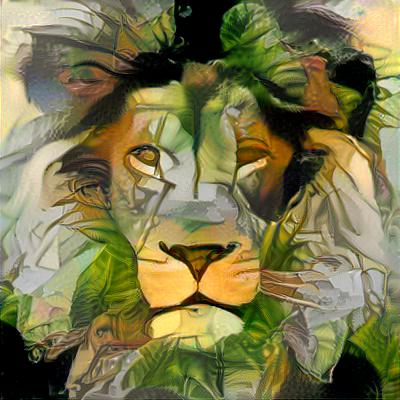
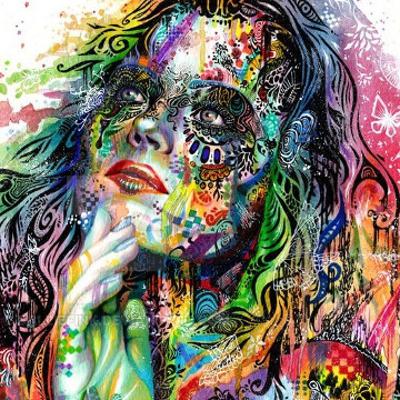
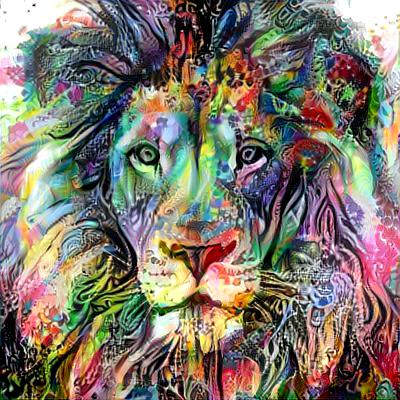
C++ implementation of neural networks library with Keras-like API. Contains majority of commonly used layers, losses and optimizers. Supports sequential and multi-input-output (flow) models. Supports single CPU, Multi-CPU and GPU tensor operations (using cuDNN and cuBLAS). This is a result of months of scouring internet for information regarding minute details of how neural networks work. Hopefully, it serves a good source of knowlegde for those who want to understand how neural networks are implemented. Master branch contains computational graphs approach allowing more complex networks. It might be easier to start your adventure analysing "classic" feed forward/backward propagate implementation available in non-computational-graph-impl branch.
Supported layers:
- Dense
- Conv2D
- Conv2DTranspose
- Pooling2D
- UpSampling2D
- BatchNormalization
- InstanceNormalization
- Value/ReflectPadding2D
- Dropout
- Flatten
- Reshape
- Concatenate
- Merge
- Activation
Supported optimizers:
- SGD
- Adam
- L-BFGS
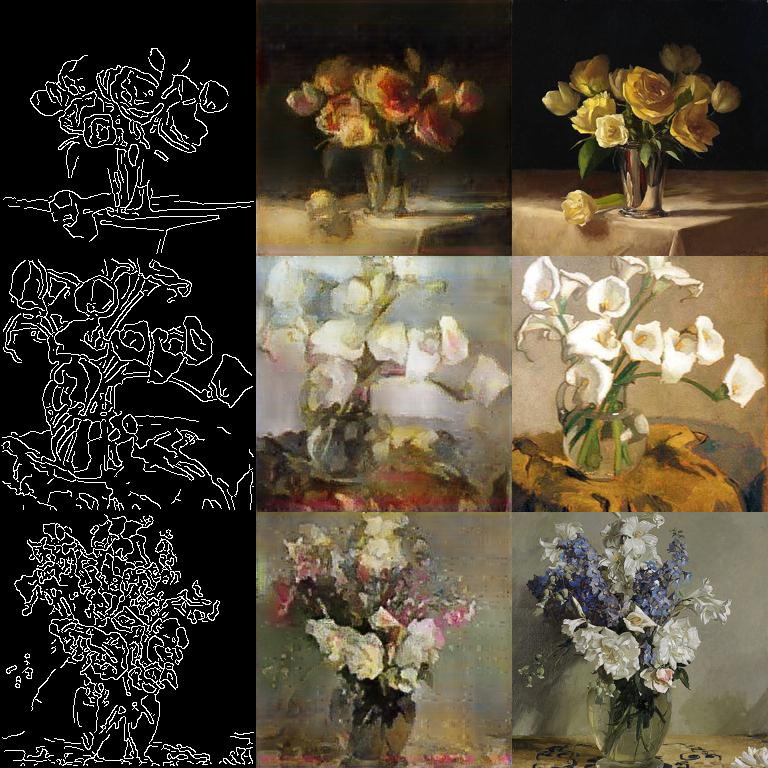
This is one of the conditional adversarial generative networks. Example below comes from training a network on a dataset of flower paintings scoured from pintrest. The goal of this particular model is to learn how to generate flower paintings from image containing only edges. Left image is conditional input to the model (created by running canny edge detection on an image from the dataset), right image is the original image from the dataset and central image is the output from generator network.
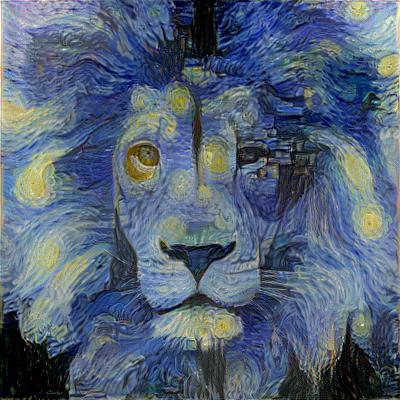
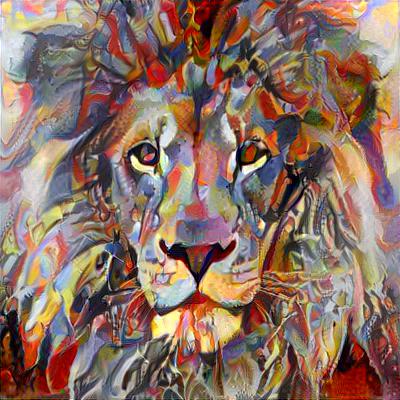
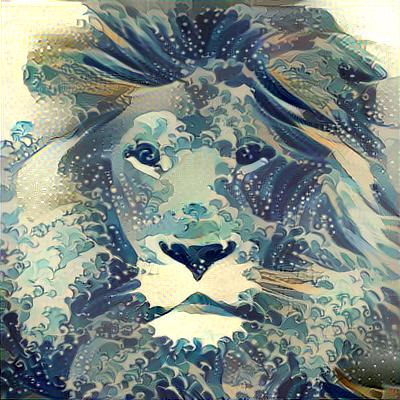
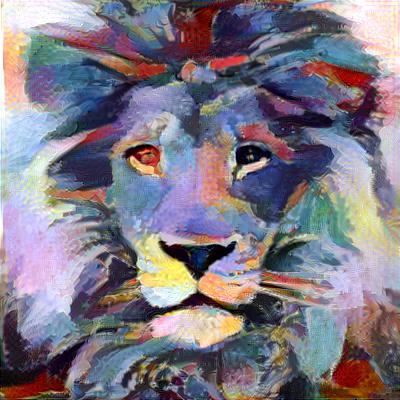
This neural network is given style image and any image we want to stylize. Model is using pre-trained VGG16/19 network to extract feature maps from style and content image and uses them to compute style and content loss. The only trainable element of the whole model is input image itself.
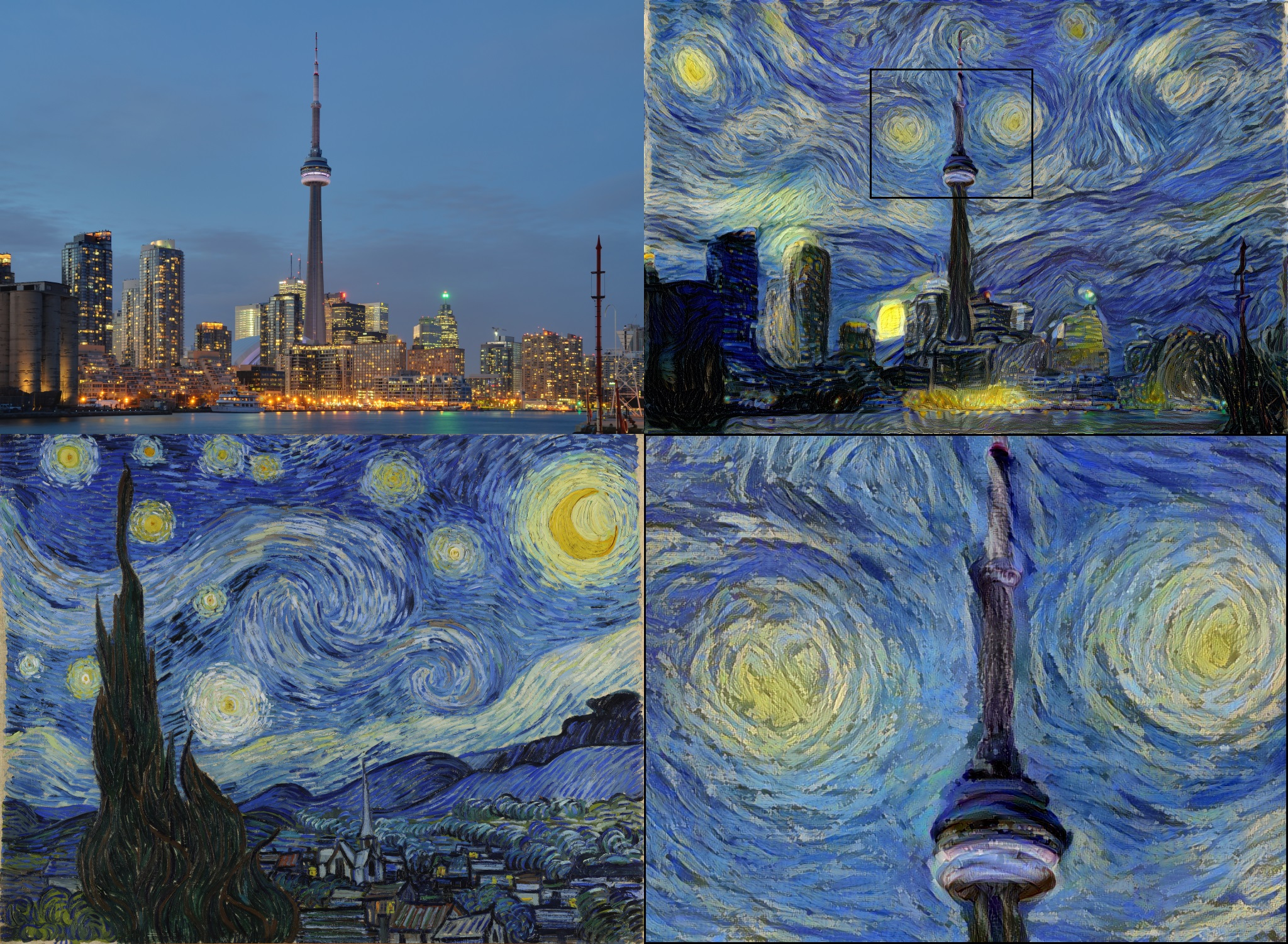
While neural style transfer is rather straight forward for small images, memory limitations of GPUs are usually disallowing going over 1280px (in case of 12GB GPUs). Because I have full control of what is happening inside my library I came up with an approach allowing me to generate 4096px resolution images using up to 4GB available on my GPU.
Deep autoencoder is trying to reduce input to small set of numbers (encode) and then try to recover the original input (decode). In the case below we go from 784 down to 392 and back to 784.
auto encoder = new Sequential("encoder");
encoder->AddLayer(new Conv2D(Shape(28, 28, 1), 3, 16, 1, 1, new ReLU()));
encoder->AddLayer(new MaxPooling2D(2, 2));
encoder->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 8, 1, 1, new ReLU()));
encoder->AddLayer(new MaxPooling2D(2, 2));
auto decoder = new Sequential("decoder");
decoder->AddLayer(new Conv2D(Shape(7, 7, 8), 3, 8, 1, 1, new ReLU()));
decoder->AddLayer(new UpSampling2D(2));
decoder->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 16, 1, 1, new ReLU()));
decoder->AddLayer(new UpSampling2D(2));
decoder->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 1, 1, 1, new Sigmoid()));
auto model = Sequential("conv_autoencoder");
model.AddLayer(encoder);
model.AddLayer(decoder);
model.Optimize(new Adam(), new BinaryCrossEntropy());
cout << model.Summary();
Tensor input, output;
LoadMnistData("data/train-images.idx3-ubyte", "data/train-labels.idx1-ubyte", input, output, true);
model.Fit(input, input, 256, 20, nullptr, nullptr, 2, TrainError);
cout << model.TrainSummary();Below are original and decoded sample digits.
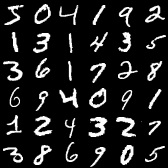
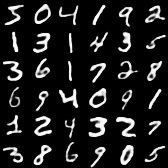
DCGAN is trying to learn to generate data samples similar to the ones it was trained on. It is comprised of 2 connected neural networks (generator and discriminator). Generator is trying to learn to generate realistic data from random noise while discriminator is learning to distinquish real from fake data.
Tensor images, labels;
LoadCifar10Data("data/cifar10_data.bin", images, labels, false);
images.Map([](float x) { return (x - 127.5f) / 127.5f; }, images);
auto dModel = new Sequential("discriminator");
dModel->AddLayer(new Conv2D(Shape(32, 32, 3), 3, 64, 2, Tensor::GetPadding(Same, 3), new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
dModel->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 128, 2, Tensor::GetPadding(Same, 3), new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
dModel->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 128, 2, Tensor::GetPadding(Same, 3), new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
dModel->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 256, 1, Tensor::GetPadding(Same, 3), new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
dModel->AddLayer(new Flatten());
dModel->AddLayer(new Dropout(0.4f));
dModel->AddLayer(new Dense(1, new Sigmoid()));
dModel->Optimize(new Adam(0.0002f, 0.5f), new BinaryCrossEntropy());
auto gModel = new Sequential("generator");
gModel->AddLayer(new Dense(100, 256*4*4, new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
gModel->AddLayer(new Reshape(Shape(4, 4, 256)));
gModel->AddLayer(new Conv2DTranspose(4, 128, 2, 1, new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
gModel->AddLayer(new Conv2DTranspose(4, 128, 2, 1, new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
gModel->AddLayer(new Conv2DTranspose(4, 128, 2, 1, new LeakyReLU(0.2f)));
gModel->AddLayer(new Conv2D(3, 3, 1, Tensor::GetPadding(Same, 3), new Tanh()));
cout << gModel->Summary();
auto ganModel = new Sequential("cifar_gan");
ganModel->AddLayer(gModel);
ganModel->AddLayer(dModel);
ganModel->Optimize(new Adam(0.0002f, 0.5f), new BinaryCrossEntropy());
const uint32_t BATCH_SIZE = 128;
const uint32_t EPOCHS = 100;
const uint32_t BATCHES_PER_EPOCH = images.Batch() / BATCH_SIZE;
Tensor real(Shape::From(dModel->OutputShape(), BATCH_SIZE)); real.FillWithValue(1.f);
Tensor fake(Shape::From(dModel->OutputShape(), BATCH_SIZE)); fake.FillWithValue(0.f);
Tensor noise(Shape::From(gModel->InputShape(), BATCH_SIZE));
for (uint32_t e = 1; e <= EPOCHS; ++e)
{
cout << "Epoch " << e << endl;
for (uint32_t i = 1; i <= BATCHES_PER_EPOCH; ++i)
{
noise.FillWithFunc([]() { return Normal::NextSingle(0, 1); });
Tensor fakeImages = gModel->Predict(noise)[0];
Tensor realImages = images.GetRandomBatches(BATCH_SIZE);
dModel->SetTrainable(true);
auto realTrainRes = dModel->TrainOnBatch(realImages, real);
auto fakeTrainRes = dModel->TrainOnBatch(fakeImages, fake);
dModel->SetTrainable(false);
auto ganTrainRes = ganModel->TrainOnBatch(noise, real);
cout << ">" << e << ", " << i << "/" << BATCHES_PER_EPOCH << setprecision(4) << fixed
<< " d1=" << get<0>(realTrainRes) << " d2=" << get<0>(fakeTrainRes)
<< " g=" << get<0>(ganTrainRes) << endl;
}
}Below are randomly generated images after 100 epochs.

Training data required to run some examples can be downloaded via this link https://www.dropbox.com/s/1zccfhtx9zi52mf/neuro_examples_data.zip Among others it contains MNIST, CIFAR-10 data sets. Other datasets like coco or wikiart can be easily googled and downloaded as they take a lot of space.
Currently CUDA, CuDNN and MKL are required to compile the library. Detailed library requirements:
- CUDA 10.1 (https://developer.nvidia.com/cuda-downloads)
- CudNN 7.6.4 (https://developer.nvidia.com/cudnn)
- Intel MKL 2019 Update 5 (https://software.intel.com/en-us/mkl/choose-download/windows)
- HDF5 (https://www.hdfgroup.org/downloads)
MKL and HDF5 dependancies are inlcuded in the Neuro library. You need to unpack deps.zip into Neuro folder in order to be able to compile the library.
Lastly, please make sure your graphics card drivers are up to date.
















