An extremely fast Python linter, written in Rust.
Linting the CPython codebase from scratch.
- ⚡️ 10-100x faster than existing linters
- 🐍 Installable via
pip - 🤝 Python 3.11 compatibility
- 🛠️
pyproject.tomlsupport - 📦 Built-in caching, to avoid re-analyzing unchanged files
- 🔧 Autofix support, for automatic error correction (e.g., automatically remove unused imports)
- ⚖️ Near-parity with the built-in Flake8 rule set
- 🔌 Native re-implementations of dozens of Flake8 plugins, like
flake8-bugbear - ⌨️ First-party editor integrations for VS Code and more
- 🌎 Monorepo-friendly, with hierarchical and cascading configuration
Ruff aims to be orders of magnitude faster than alternative tools while integrating more functionality behind a single, common interface.
Ruff can be used to replace Flake8 (plus a variety of plugins), isort,
pydocstyle, yesqa,
eradicate, pyupgrade,
and autoflake, all while executing tens or hundreds of
times faster than any individual tool.
Ruff goes beyond the responsibilities of a traditional linter, instead functioning as an advanced code transformation tool capable of upgrading type annotations, rewriting class definitions, sorting imports, and more.
Ruff is extremely actively developed and used in major open-source projects like:
- pandas
- FastAPI
- Apache Airflow
- Bokeh
- Zulip
- Pydantic
- Dagster
- Dagger
- Sphinx
- Hatch
- Jupyter
- Great Expectations
- Polars
- Ibis
- Synapse (Matrix)
- SnowCLI (Snowflake)
- Saleor
- OpenBB
- Home Assistant
- Cryptography (PyCA)
- cibuildwheel (PyPA)
- Babel
Read the launch blog post.
Sebastián Ramírez, creator of FastAPI:
Ruff is so fast that sometimes I add an intentional bug in the code just to confirm it's actually running and checking the code.
Nick Schrock, founder of Elementl, co-creator of GraphQL:
Why is Ruff a gamechanger? Primarily because it is nearly 1000x faster. Literally. Not a typo. On our largest module (dagster itself, 250k LOC) pylint takes about 2.5 minutes, parallelized across 4 cores on my M1. Running ruff against our entire codebase takes .4 seconds.
Bryan Van de Ven, co-creator of Bokeh, original author of Conda:
Ruff is ~150-200x faster than flake8 on my machine, scanning the whole repo takes ~0.2s instead of ~20s. This is an enormous quality of life improvement for local dev. It's fast enough that I added it as an actual commit hook, which is terrific.
Timothy Crosley, creator of isort:
Just switched my first project to Ruff. Only one downside so far: it's so fast I couldn't believe it was working till I intentionally introduced some errors.
Tim Abbott, lead developer of Zulip:
This is just ridiculously fast...
ruffis amazing.
- Installation and Usage
- Configuration
- Supported Rules
- Pyflakes (F)
- pycodestyle (E, W)
- mccabe (C90)
- isort (I)
- pydocstyle (D)
- pyupgrade (UP)
- pep8-naming (N)
- flake8-2020 (YTT)
- flake8-annotations (ANN)
- flake8-bandit (S)
- flake8-blind-except (BLE)
- flake8-boolean-trap (FBT)
- flake8-bugbear (B)
- flake8-builtins (A)
- flake8-comprehensions (C4)
- flake8-debugger (T10)
- flake8-errmsg (EM)
- flake8-implicit-str-concat (ISC)
- flake8-import-conventions (ICN)
- flake8-print (T20)
- flake8-pytest-style (PT)
- flake8-quotes (Q)
- flake8-return (RET)
- flake8-simplify (SIM)
- flake8-tidy-imports (TID)
- flake8-unused-arguments (ARG)
- flake8-datetimez (DTZ)
- eradicate (ERA)
- pandas-vet (PD)
- pygrep-hooks (PGH)
- Pylint (PL)
- flake8-pie (PIE)
- flake8-commas (COM)
- flake8-no-pep420 (INP)
- flake8-executable (EXE)
- flake8-type-checking (TCH)
- tryceratops (TRY)
- flake8-use-pathlib (PTH)
- Ruff-specific rules (RUF)
- Editor Integrations
- FAQ
- Contributing
- Releases
- Benchmarks
- Reference
- License
Ruff is available as ruff on PyPI:
pip install ruffFor macOS Homebrew and Linuxbrew users, Ruff is also available as ruff on Homebrew:
brew install ruffFor Conda users, Ruff is also available as ruff on conda-forge:
conda install -c conda-forge ruffFor Arch Linux users, Ruff is also available as ruff on the official repositories:
pacman -S ruffFor Alpine users, Ruff is also available as ruff on the testing repositories:
apk add ruffTo run Ruff, try any of the following:
ruff path/to/code/to/lint.py # Run Ruff over `lint.py`
ruff path/to/code/ # Run Ruff over all files in `/path/to/code` (and any subdirectories)
ruff path/to/code/*.py # Run Ruff over all `.py` files in `/path/to/code`You can run Ruff in --watch mode to automatically re-run on-change:
ruff path/to/code/ --watchRuff also works with pre-commit:
- repo: https://github.com/charliermarsh/ruff-pre-commit
# Ruff version.
rev: 'v0.0.235'
hooks:
- id: ruffRuff is configurable both via pyproject.toml and the command line. For a full list of configurable
options, see the API reference.
If left unspecified, the default configuration is equivalent to:
[tool.ruff]
line-length = 88
# Enable Pyflakes `E` and `F` codes by default.
select = ["E", "F"]
ignore = []
# Exclude a variety of commonly ignored directories.
exclude = [
".bzr",
".direnv",
".eggs",
".git",
".hg",
".mypy_cache",
".nox",
".pants.d",
".ruff_cache",
".svn",
".tox",
".venv",
"__pypackages__",
"_build",
"buck-out",
"build",
"dist",
"node_modules",
"venv",
]
per-file-ignores = {}
# Allow unused variables when underscore-prefixed.
dummy-variable-rgx = "^(_+|(_+[a-zA-Z0-9_]*[a-zA-Z0-9]+?))$"
# Assume Python 3.10.
target-version = "py310"
[tool.ruff.mccabe]
# Unlike Flake8, default to a complexity level of 10.
max-complexity = 10As an example, the following would configure Ruff to: (1) avoid enforcing line-length violations
(E501); (2) never remove unused imports (F401); and (3) ignore import-at-top-of-file violations
(E402) in __init__.py files:
[tool.ruff]
# Enable Pyflakes and pycodestyle rules.
select = ["E", "F"]
# Never enforce `E501` (line length violations).
ignore = ["E501"]
# Never try to fix `F401` (unused imports).
unfixable = ["F401"]
# Ignore `E402` (import violations) in all `__init__.py` files, and in `path/to/file.py`.
[tool.ruff.per-file-ignores]
"__init__.py" = ["E402"]
"path/to/file.py" = ["E402"]Plugin configurations should be expressed as subsections, e.g.:
[tool.ruff]
# Add "Q" to the list of enabled codes.
select = ["E", "F", "Q"]
[tool.ruff.flake8-quotes]
docstring-quotes = "double"Ruff mirrors Flake8's rule code system, in which each rule code consists of a one-to-three letter
prefix, followed by three digits (e.g., F401). The prefix indicates that "source" of the rule
(e.g., F for Pyflakes, E for pycodestyle, ANN for flake8-annotations). The set of enabled
rules is determined by the select and ignore options, which support both the full code (e.g.,
F401) and the prefix (e.g., F).
As a special-case, Ruff also supports the ALL code, which enables all rules. Note that some of the
pydocstyle rules conflict (e.g., D203 and D211) as they represent alternative docstring
formats. Enabling ALL without further configuration may result in suboptimal behavior, especially
for the pydocstyle plugin.
As an alternative to pyproject.toml, Ruff will also respect a ruff.toml file, which implements
an equivalent schema (though the [tool.ruff] hierarchy can be omitted). For example, the
pyproject.toml described above would be represented via the following ruff.toml:
# Enable Pyflakes and pycodestyle rules.
select = ["E", "F"]
# Never enforce `E501` (line length violations).
ignore = ["E501"]
# Always autofix, but never try to fix `F401` (unused imports).
fix = true
unfixable = ["F401"]
# Ignore `E402` (import violations) in all `__init__.py` files, and in `path/to/file.py`.
[per-file-ignores]
"__init__.py" = ["E402"]
"path/to/file.py" = ["E402"]For a full list of configurable options, see the API reference.
Some common configuration settings can be provided via the command-line:
ruff path/to/code/ --select F401 --select F403See ruff --help for more:
Ruff: An extremely fast Python linter.
Usage: ruff [OPTIONS] [FILES]...
Arguments:
[FILES]...
Options:
--config <CONFIG>
Path to the `pyproject.toml` or `ruff.toml` file to use for configuration
-v, --verbose
Enable verbose logging
-q, --quiet
Print lint violations, but nothing else
-s, --silent
Disable all logging (but still exit with status code "1" upon detecting lint violations)
-e, --exit-zero
Exit with status code "0", even upon detecting lint violations
-w, --watch
Run in watch mode by re-running whenever files change
--fix
Attempt to automatically fix lint violations
--fix-only
Fix any fixable lint violations, but don't report on leftover violations. Implies `--fix`
--diff
Avoid writing any fixed files back; instead, output a diff for each changed file to stdout
-n, --no-cache
Disable cache reads
--isolated
Ignore all configuration files
--select <RULE_CODE>
Comma-separated list of rule codes to enable (or ALL, to enable all rules)
--extend-select <RULE_CODE>
Like --select, but adds additional rule codes on top of the selected ones
--ignore <RULE_CODE>
Comma-separated list of rule codes to disable
--extend-ignore <RULE_CODE>
Like --ignore, but adds additional rule codes on top of the ignored ones
--exclude <FILE_PATTERN>
List of paths, used to omit files and/or directories from analysis
--extend-exclude <FILE_PATTERN>
Like --exclude, but adds additional files and directories on top of those already excluded
--fixable <RULE_CODE>
List of rule codes to treat as eligible for autofix. Only applicable when autofix itself is enabled (e.g., via `--fix`)
--unfixable <RULE_CODE>
List of rule codes to treat as ineligible for autofix. Only applicable when autofix itself is enabled (e.g., via `--fix`)
--per-file-ignores <PER_FILE_IGNORES>
List of mappings from file pattern to code to exclude
--format <FORMAT>
Output serialization format for violations [env: RUFF_FORMAT=] [possible values: text, json, junit, grouped, github, gitlab, pylint]
--stdin-filename <STDIN_FILENAME>
The name of the file when passing it through stdin
--cache-dir <CACHE_DIR>
Path to the cache directory [env: RUFF_CACHE_DIR=]
--show-source
Show violations with source code
--respect-gitignore
Respect file exclusions via `.gitignore` and other standard ignore files
--force-exclude
Enforce exclusions, even for paths passed to Ruff directly on the command-line
--update-check
Enable or disable automatic update checks
--dummy-variable-rgx <DUMMY_VARIABLE_RGX>
Regular expression matching the name of dummy variables
--target-version <TARGET_VERSION>
The minimum Python version that should be supported
--line-length <LINE_LENGTH>
Set the line-length for length-associated rules and automatic formatting
--add-noqa
Enable automatic additions of `noqa` directives to failing lines
--clean
Clear any caches in the current directory or any subdirectories
--explain <EXPLAIN>
Explain a rule
--show-files
See the files Ruff will be run against with the current settings
--show-settings
See the settings Ruff will use to lint a given Python file
-h, --help
Print help
-V, --version
Print version
Similar to ESLint,
Ruff supports hierarchical configuration, such that the "closest" pyproject.toml file in the
directory hierarchy is used for every individual file, with all paths in the pyproject.toml file
(e.g., exclude globs, src paths) being resolved relative to the directory containing the
pyproject.toml file.
There are a few exceptions to these rules:
- In locating the "closest"
pyproject.tomlfile for a given path, Ruff ignores anypyproject.tomlfiles that lack a[tool.ruff]section. - If a configuration file is passed directly via
--config, those settings are used for across files. Any relative paths in that configuration file (likeexcludeglobs orsrcpaths) are resolved relative to the current working directory. - If no
pyproject.tomlfile is found in the filesystem hierarchy, Ruff will fall back to using a default configuration. If a user-specific configuration file exists at${config_dir}/ruff/pyproject.toml, that file will be used instead of the default configuration, with${config_dir}being determined via thedirscrate, and all relative paths being again resolved relative to the current working directory. - Any
pyproject.toml-supported settings that are provided on the command-line (e.g., via--select) will override the settings in every resolved configuration file.
Unlike ESLint,
Ruff does not merge settings across configuration files; instead, the "closest" configuration file
is used, and any parent configuration files are ignored. In lieu of this implicit cascade, Ruff
supports an extend field, which allows you to inherit the settings from another
pyproject.toml file, like so:
# Extend the `pyproject.toml` file in the parent directory.
extend = "../pyproject.toml"
# But use a different line length.
line-length = 100All of the above rules apply equivalently to ruff.toml files. If Ruff detects both a ruff.toml
and pyproject.toml file, it will defer to the ruff.toml.
When passed a path on the command-line, Ruff will automatically discover all Python files in that
path, taking into account the exclude and extend-exclude settings
in each directory's pyproject.toml file.
By default, Ruff will also skip any files that are omitted via .ignore, .gitignore,
.git/info/exclude, and global gitignore files (see: respect-gitignore).
Files that are passed to ruff directly are always linted, regardless of the above criteria.
For example, ruff /path/to/excluded/file.py will always lint file.py.
To omit a lint rule entirely, add it to the "ignore" list via ignore or
extend-ignore, either on the command-line or in your pyproject.toml file.
To ignore a violation inline, Ruff uses a noqa system similar to Flake8.
To ignore an individual violation, add # noqa: {code} to the end of the line, like so:
# Ignore F841.
x = 1 # noqa: F841
# Ignore E741 and F841.
i = 1 # noqa: E741, F841
# Ignore _all_ violations.
x = 1 # noqaNote that, for multi-line strings, the noqa directive should come at the end of the string, and
will apply to the entire string, like so:
"""Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, consectetur adipiscing elit, sed do eiusmod tempor incididunt ut labore et dolore magna aliqua.
""" # noqa: E501To ignore all violations across an entire file, Ruff supports Flake8's # flake8: noqa directive
(or, equivalently, # ruff: noqa). Adding either of those directives to any part of a file will
disable enforcement across the entire file.
For targeted exclusions across entire files (e.g., "Ignore all F841 violations in
/path/to/file.py"), see the per-file-ignores configuration setting.
Ruff respects isort's "Action Comments"
(# isort: skip_file, # isort: on, # isort: off, # isort: skip, and # isort: split), which
enable selectively enabling and disabling import sorting for blocks of code and other inline
configuration.
See the isort documentation
for more.
Ruff supports several workflows to aid in noqa management.
First, Ruff provides a special rule code, RUF100, to enforce that your noqa directives are
"valid", in that the violations they say they ignore are actually being triggered on that line (and
thus suppressed). You can run ruff /path/to/file.py --extend-select RUF100 to flag unused noqa
directives.
Second, Ruff can automatically remove unused noqa directives via its autofix functionality.
You can run ruff /path/to/file.py --extend-select RUF100 --fix to automatically remove unused
noqa directives.
Third, Ruff can automatically add noqa directives to all failing lines. This is useful when
migrating a new codebase to Ruff. You can run ruff /path/to/file.py --add-noqa to automatically
add noqa directives to all failing lines, with the appropriate rule codes.
Regardless of the rule's origin, Ruff re-implements every rule in Rust as a first-party feature.
By default, Ruff enables all E and F rule codes, which correspond to those built-in to Flake8.
The 🛠 emoji indicates that a rule is automatically fixable by the --fix command-line option.
For more, see Pyflakes on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| F401 | unused-import | {name} imported but unused; consider adding to __all__ or using a redundant alias |
🛠 |
| F402 | import-shadowed-by-loop-var | Import {name} from line {line} shadowed by loop variable |
|
| F403 | import-star-used | from {name} import * used; unable to detect undefined names |
|
| F404 | late-future-import | from __future__ imports must occur at the beginning of the file |
|
| F405 | import-star-usage | {name} may be undefined, or defined from star imports: {sources} |
|
| F406 | import-star-not-permitted | from {name} import * only allowed at module level |
|
| F407 | future-feature-not-defined | Future feature {name} is not defined |
|
| F501 | percent-format-invalid-format | '...' % ... has invalid format string: {message} | |
| F502 | percent-format-expected-mapping | '...' % ... expected mapping but got sequence | |
| F503 | percent-format-expected-sequence | '...' % ... expected sequence but got mapping | |
| F504 | percent-format-extra-named-arguments | '...' % ... has unused named argument(s): {message} | 🛠 |
| F505 | percent-format-missing-argument | '...' % ... is missing argument(s) for placeholder(s): {message} | |
| F506 | percent-format-mixed-positional-and-named | '...' % ... has mixed positional and named placeholders | |
| F507 | percent-format-positional-count-mismatch | '...' % ... has {wanted} placeholder(s) but {got} substitution(s) | |
| F508 | percent-format-star-requires-sequence | '...' % ... * specifier requires sequence |
|
| F509 | percent-format-unsupported-format-character | '...' % ... has unsupported format character '{char}' | |
| F521 | string-dot-format-invalid-format | '...'.format(...) has invalid format string: {message} | |
| F522 | string-dot-format-extra-named-arguments | '...'.format(...) has unused named argument(s): {message} | 🛠 |
| F523 | string-dot-format-extra-positional-arguments | '...'.format(...) has unused arguments at position(s): {message} | |
| F524 | string-dot-format-missing-arguments | '...'.format(...) is missing argument(s) for placeholder(s): {message} | |
| F525 | string-dot-format-mixing-automatic | '...'.format(...) mixes automatic and manual numbering | |
| F541 | f-string-missing-placeholders | f-string without any placeholders | 🛠 |
| F601 | multi-value-repeated-key-literal | Dictionary key literal {name} repeated |
🛠 |
| F602 | multi-value-repeated-key-variable | Dictionary key {name} repeated |
🛠 |
| F621 | expressions-in-star-assignment | Too many expressions in star-unpacking assignment | |
| F622 | two-starred-expressions | Two starred expressions in assignment | |
| F631 | assert-tuple | Assert test is a non-empty tuple, which is always True |
|
| F632 | is-literal | Use == to compare constant literals |
🛠 |
| F633 | invalid-print-syntax | Use of >> is invalid with print function |
|
| F634 | if-tuple | If test is a tuple, which is always True |
|
| F701 | break-outside-loop | break outside loop |
|
| F702 | continue-outside-loop | continue not properly in loop |
|
| F704 | yield-outside-function | {keyword} statement outside of a function |
|
| F706 | return-outside-function | return statement outside of a function/method |
|
| F707 | default-except-not-last | An except block as not the last exception handler |
|
| F722 | forward-annotation-syntax-error | Syntax error in forward annotation: {body} |
|
| F811 | redefined-while-unused | Redefinition of unused {name} from line {line} |
|
| F821 | undefined-name | Undefined name {name} |
|
| F822 | undefined-export | Undefined name {name} in __all__ |
|
| F823 | undefined-local | Local variable {name} referenced before assignment |
|
| F841 | unused-variable | Local variable {name} is assigned to but never used |
🛠 |
| F842 | unused-annotation | Local variable {name} is annotated but never used |
|
| F901 | raise-not-implemented | raise NotImplemented should be raise NotImplementedError |
🛠 |
For more, see pycodestyle on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| E101 | mixed-spaces-and-tabs | Indentation contains mixed spaces and tabs | |
| E401 | multiple-imports-on-one-line | Multiple imports on one line | |
| E402 | module-import-not-at-top-of-file | Module level import not at top of file | |
| E501 | line-too-long | Line too long ({length} > {limit} characters) | |
| E711 | none-comparison | Comparison to None should be cond is None |
🛠 |
| E712 | true-false-comparison | Comparison to True should be cond is True |
🛠 |
| E713 | not-in-test | Test for membership should be not in |
🛠 |
| E714 | not-is-test | Test for object identity should be is not |
🛠 |
| E721 | type-comparison | Do not compare types, use isinstance() |
|
| E722 | do-not-use-bare-except | Do not use bare except |
|
| E731 | do-not-assign-lambda | Do not assign a lambda expression, use a def |
🛠 |
| E741 | ambiguous-variable-name | Ambiguous variable name: {name} |
|
| E742 | ambiguous-class-name | Ambiguous class name: {name} |
|
| E743 | ambiguous-function-name | Ambiguous function name: {name} |
|
| E902 | io-error | {message} | |
| E999 | syntax-error | SyntaxError: {message} |
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| W292 | no-new-line-at-end-of-file | No newline at end of file | 🛠 |
| W505 | doc-line-too-long | Doc line too long ({length} > {limit} characters) | |
| W605 | invalid-escape-sequence | Invalid escape sequence: '{char}' | 🛠 |
For more, see mccabe on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| C901 | function-is-too-complex | {name} is too complex ({complexity}) |
For more, see isort on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| I001 | unsorted-imports | Import block is un-sorted or un-formatted | 🛠 |
| I002 | missing-required-import | Missing required import: {name} |
🛠 |
For more, see pydocstyle on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| D100 | public-module | Missing docstring in public module | |
| D101 | public-class | Missing docstring in public class | |
| D102 | public-method | Missing docstring in public method | |
| D103 | public-function | Missing docstring in public function | |
| D104 | public-package | Missing docstring in public package | |
| D105 | magic-method | Missing docstring in magic method | |
| D106 | public-nested-class | Missing docstring in public nested class | |
| D107 | public-init | Missing docstring in __init__ |
|
| D200 | fits-on-one-line | One-line docstring should fit on one line | 🛠 |
| D201 | no-blank-line-before-function | No blank lines allowed before function docstring (found {num_lines}) | 🛠 |
| D202 | no-blank-line-after-function | No blank lines allowed after function docstring (found {num_lines}) | 🛠 |
| D203 | one-blank-line-before-class | 1 blank line required before class docstring | 🛠 |
| D204 | one-blank-line-after-class | 1 blank line required after class docstring | 🛠 |
| D205 | blank-line-after-summary | 1 blank line required between summary line and description | 🛠 |
| D206 | indent-with-spaces | Docstring should be indented with spaces, not tabs | |
| D207 | no-under-indentation | Docstring is under-indented | 🛠 |
| D208 | no-over-indentation | Docstring is over-indented | 🛠 |
| D209 | new-line-after-last-paragraph | Multi-line docstring closing quotes should be on a separate line | 🛠 |
| D210 | no-surrounding-whitespace | No whitespaces allowed surrounding docstring text | 🛠 |
| D211 | no-blank-line-before-class | No blank lines allowed before class docstring | 🛠 |
| D212 | multi-line-summary-first-line | Multi-line docstring summary should start at the first line | 🛠 |
| D213 | multi-line-summary-second-line | Multi-line docstring summary should start at the second line | 🛠 |
| D214 | section-not-over-indented | Section is over-indented ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D215 | section-underline-not-over-indented | Section underline is over-indented ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D300 | uses-triple-quotes | Use """triple double quotes""" | |
| D301 | uses-r-prefix-for-backslashed-content | Use r""" if any backslashes in a docstring | |
| D400 | ends-in-period | First line should end with a period | 🛠 |
| D401 | non-imperative-mood | First line of docstring should be in imperative mood: "{first_line}" | |
| D402 | no-signature | First line should not be the function's signature | |
| D403 | first-line-capitalized | First word of the first line should be properly capitalized | |
| D404 | no-this-prefix | First word of the docstring should not be "This" | |
| D405 | capitalize-section-name | Section name should be properly capitalized ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D406 | new-line-after-section-name | Section name should end with a newline ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D407 | dashed-underline-after-section | Missing dashed underline after section ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D408 | section-underline-after-name | Section underline should be in the line following the section's name ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D409 | section-underline-matches-section-length | Section underline should match the length of its name ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D410 | blank-line-after-section | Missing blank line after section ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D411 | blank-line-before-section | Missing blank line before section ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D412 | no-blank-lines-between-header-and-content | No blank lines allowed between a section header and its content ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D413 | blank-line-after-last-section | Missing blank line after last section ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D414 | non-empty-section | Section has no content ("{name}") | |
| D415 | ends-in-punctuation | First line should end with a period, question mark, or exclamation point | 🛠 |
| D416 | section-name-ends-in-colon | Section name should end with a colon ("{name}") | 🛠 |
| D417 | document-all-arguments | Missing argument description in the docstring: {name} |
|
| D418 | skip-docstring | Function decorated with @overload shouldn't contain a docstring |
|
| D419 | non-empty | Docstring is empty |
For more, see pyupgrade on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| UP001 | useless-metaclass-type | __metaclass__ = type is implied |
🛠 |
| UP003 | type-of-primitive | Use {} instead of type(...) |
🛠 |
| UP004 | useless-object-inheritance | Class {name} inherits from object |
🛠 |
| UP005 | deprecated-unittest-alias | {alias} is deprecated, use {target} |
🛠 |
| UP006 | use-pep585-annotation | Use {} instead of {} for type annotations |
🛠 |
| UP007 | use-pep604-annotation | Use X | Y for type annotations |
🛠 |
| UP008 | super-call-with-parameters | Use super() instead of super(__class__, self) |
🛠 |
| UP009 | pep3120-unnecessary-coding-comment | UTF-8 encoding declaration is unnecessary | 🛠 |
| UP010 | unnecessary-future-import | Unnecessary __future__ import {import} for target Python version |
🛠 |
| UP011 | lru-cache-without-parameters | Unnecessary parameters to functools.lru_cache |
🛠 |
| UP012 | unnecessary-encode-utf8 | Unnecessary call to encode as UTF-8 |
🛠 |
| UP013 | convert-typed-dict-functional-to-class | Convert {name} from TypedDict functional to class syntax |
🛠 |
| UP014 | convert-named-tuple-functional-to-class | Convert {name} from NamedTuple functional to class syntax |
🛠 |
| UP015 | redundant-open-modes | Unnecessary open mode parameters | 🛠 |
| UP016 | remove-six-compat | Unnecessary six compatibility usage |
🛠 |
| UP017 | datetime-timezone-utc | Use datetime.UTC alias |
🛠 |
| UP018 | native-literals | Unnecessary call to {literal_type} |
🛠 |
| UP019 | typing-text-str-alias | typing.Text is deprecated, use str |
🛠 |
| UP020 | open-alias | Use builtin open |
🛠 |
| UP021 | replace-universal-newlines | universal_newlines is deprecated, use text |
🛠 |
| UP022 | replace-stdout-stderr | Sending stdout and stderr to pipe is deprecated, use capture_output |
🛠 |
| UP023 | rewrite-c-element-tree | cElementTree is deprecated, use ElementTree |
🛠 |
| UP024 | os-error-alias | Replace aliased errors with OSError |
🛠 |
| UP025 | rewrite-unicode-literal | Remove unicode literals from strings | 🛠 |
| UP026 | rewrite-mock-import | mock is deprecated, use unittest.mock |
🛠 |
| UP027 | rewrite-list-comprehension | Replace unpacked list comprehension with a generator expression | 🛠 |
| UP028 | rewrite-yield-from | Replace yield over for loop with yield from |
🛠 |
| UP029 | unnecessary-builtin-import | Unnecessary builtin import: {import} |
🛠 |
| UP030 | format-literals | Use implicit references for positional format fields | 🛠 |
| UP031 | printf-string-formatting | Use format specifiers instead of percent format | 🛠 |
| UP032 | f-string | Use f-string instead of format call |
🛠 |
| UP033 | functools-cache | Use @functools.cache instead of @functools.lru_cache(maxsize=None) |
🛠 |
| UP034 | extraneous-parentheses | Avoid extraneous parentheses | 🛠 |
For more, see pep8-naming on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| N801 | invalid-class-name | Class name {name} should use CapWords convention |
|
| N802 | invalid-function-name | Function name {name} should be lowercase |
|
| N803 | invalid-argument-name | Argument name {name} should be lowercase |
|
| N804 | invalid-first-argument-name-for-class-method | First argument of a class method should be named cls |
|
| N805 | invalid-first-argument-name-for-method | First argument of a method should be named self |
|
| N806 | non-lowercase-variable-in-function | Variable {name} in function should be lowercase |
|
| N807 | dunder-function-name | Function name should not start and end with __ |
|
| N811 | constant-imported-as-non-constant | Constant {name} imported as non-constant {asname} |
|
| N812 | lowercase-imported-as-non-lowercase | Lowercase {name} imported as non-lowercase {asname} |
|
| N813 | camelcase-imported-as-lowercase | Camelcase {name} imported as lowercase {asname} |
|
| N814 | camelcase-imported-as-constant | Camelcase {name} imported as constant {asname} |
|
| N815 | mixed-case-variable-in-class-scope | Variable {name} in class scope should not be mixedCase |
|
| N816 | mixed-case-variable-in-global-scope | Variable {name} in global scope should not be mixedCase |
|
| N817 | camelcase-imported-as-acronym | Camelcase {name} imported as acronym {asname} |
|
| N818 | error-suffix-on-exception-name | Exception name {name} should be named with an Error suffix |
For more, see flake8-2020 on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| YTT101 | sys-version-slice3-referenced | sys.version[:3] referenced (python3.10), use sys.version_info |
|
| YTT102 | sys-version2-referenced | sys.version[2] referenced (python3.10), use sys.version_info |
|
| YTT103 | sys-version-cmp-str3 | sys.version compared to string (python3.10), use sys.version_info |
|
| YTT201 | sys-version-info0-eq3-referenced | sys.version_info[0] == 3 referenced (python4), use >= |
|
| YTT202 | six-py3-referenced | six.PY3 referenced (python4), use not six.PY2 |
|
| YTT203 | sys-version-info1-cmp-int | sys.version_info[1] compared to integer (python4), compare sys.version_info to tuple |
|
| YTT204 | sys-version-info-minor-cmp-int | sys.version_info.minor compared to integer (python4), compare sys.version_info to tuple |
|
| YTT301 | sys-version0-referenced | sys.version[0] referenced (python10), use sys.version_info |
|
| YTT302 | sys-version-cmp-str10 | sys.version compared to string (python10), use sys.version_info |
|
| YTT303 | sys-version-slice1-referenced | sys.version[:1] referenced (python10), use sys.version_info |
For more, see flake8-annotations on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| ANN001 | missing-type-function-argument | Missing type annotation for function argument {name} |
|
| ANN002 | missing-type-args | Missing type annotation for *{name} |
|
| ANN003 | missing-type-kwargs | Missing type annotation for **{name} |
|
| ANN101 | missing-type-self | Missing type annotation for {name} in method |
|
| ANN102 | missing-type-cls | Missing type annotation for {name} in classmethod |
|
| ANN201 | missing-return-type-public-function | Missing return type annotation for public function {name} |
|
| ANN202 | missing-return-type-private-function | Missing return type annotation for private function {name} |
|
| ANN204 | missing-return-type-special-method | Missing return type annotation for special method {name} |
🛠 |
| ANN205 | missing-return-type-static-method | Missing return type annotation for staticmethod {name} |
|
| ANN206 | missing-return-type-class-method | Missing return type annotation for classmethod {name} |
|
| ANN401 | dynamically-typed-expression | Dynamically typed expressions (typing.Any) are disallowed in {name} |
For more, see flake8-bandit on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| S101 | assert-used | Use of assert detected |
|
| S102 | exec-used | Use of exec detected |
|
| S103 | bad-file-permissions | os.chmod setting a permissive mask {mask:#o} on file or directory |
|
| S104 | hardcoded-bind-all-interfaces | Possible binding to all interfaces | |
| S105 | hardcoded-password-string | Possible hardcoded password: "{}" | |
| S106 | hardcoded-password-func-arg | Possible hardcoded password: "{}" | |
| S107 | hardcoded-password-default | Possible hardcoded password: "{}" | |
| S108 | hardcoded-temp-file | Probable insecure usage of temporary file or directory: "{}" | |
| S113 | request-without-timeout | Probable use of requests call with timeout set to {value} |
|
| S324 | hashlib-insecure-hash-function | Probable use of insecure hash functions in hashlib: "{}" |
|
| S501 | request-with-no-cert-validation | Probable use of {string} call with verify=False disabling SSL certificate checks |
|
| S506 | unsafe-yaml-load | Probable use of unsafe loader {name} with yaml.load. Allows instantiation of arbitrary objects. Consider yaml.safe_load. |
|
| S508 | snmp-insecure-version | The use of SNMPv1 and SNMPv2 is insecure. Use SNMPv3 if able. | |
| S509 | snmp-weak-cryptography | You should not use SNMPv3 without encryption. noAuthNoPriv & authNoPriv is insecure. |
|
| S612 | logging-config-insecure-listen | Use of insecure logging.config.listen detected |
|
| S701 | jinja2-autoescape-false | Using jinja2 templates with autoescape=False is dangerous and can lead to XSS. Ensure autoescape=True or use the select_autoescape function. |
For more, see flake8-blind-except on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| BLE001 | blind-except | Do not catch blind exception: {name} |
For more, see flake8-boolean-trap on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| FBT001 | boolean-positional-arg-in-function-definition | Boolean positional arg in function definition | |
| FBT002 | boolean-default-value-in-function-definition | Boolean default value in function definition | |
| FBT003 | boolean-positional-value-in-function-call | Boolean positional value in function call |
For more, see flake8-bugbear on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| B002 | unary-prefix-increment | Python does not support the unary prefix increment | |
| B003 | assignment-to-os-environ | Assigning to os.environ doesn't clear the environment |
|
| B004 | unreliable-callable-check | Using hasattr(x, '__call__') to test if x is callable is unreliable. Use callable(x) for consistent results. |
|
| B005 | strip-with-multi-characters | Using .strip() with multi-character strings is misleading the reader |
|
| B006 | mutable-argument-default | Do not use mutable data structures for argument defaults | |
| B007 | unused-loop-control-variable | Loop control variable {name} not used within loop body |
|
| B008 | function-call-argument-default | Do not perform function call {name} in argument defaults |
|
| B009 | get-attr-with-constant | Do not call getattr with a constant attribute value. It is not any safer than normal property access. |
🛠 |
| B010 | set-attr-with-constant | Do not call setattr with a constant attribute value. It is not any safer than normal property access. |
🛠 |
| B011 | do-not-assert-false | Do not assert False (python -O removes these calls), raise AssertionError() |
🛠 |
| B012 | jump-statement-in-finally | {name} inside finally blocks cause exceptions to be silenced |
|
| B013 | redundant-tuple-in-exception-handler | A length-one tuple literal is redundant. Write except {name} instead of except ({name},). |
🛠 |
| B014 | duplicate-handler-exception | Exception handler with duplicate exception: {name} |
🛠 |
| B015 | useless-comparison | Pointless comparison. This comparison does nothing but waste CPU instructions. Either prepend assert or remove it. |
|
| B016 | cannot-raise-literal | Cannot raise a literal. Did you intend to return it or raise an Exception? | |
| B017 | no-assert-raises-exception | assertRaises(Exception) should be considered evil |
|
| B018 | useless-expression | Found useless expression. Either assign it to a variable or remove it. | |
| B019 | cached-instance-method | Use of functools.lru_cache or functools.cache on methods can lead to memory leaks |
|
| B020 | loop-variable-overrides-iterator | Loop control variable {name} overrides iterable it iterates |
|
| B021 | f-string-docstring | f-string used as docstring. This will be interpreted by python as a joined string rather than a docstring. | |
| B022 | useless-contextlib-suppress | No arguments passed to contextlib.suppress. No exceptions will be suppressed and therefore this context manager is redundant |
|
| B023 | function-uses-loop-variable | Function definition does not bind loop variable {name} |
|
| B024 | abstract-base-class-without-abstract-method | {name} is an abstract base class, but it has no abstract methods |
|
| B025 | duplicate-try-block-exception | try-except block with duplicate exception {name} |
|
| B026 | star-arg-unpacking-after-keyword-arg | Star-arg unpacking after a keyword argument is strongly discouraged | |
| B027 | empty-method-without-abstract-decorator | {name} is an empty method in an abstract base class, but has no abstract decorator |
|
| B904 | raise-without-from-inside-except | Within an except clause, raise exceptions with raise ... from err or raise ... from None to distinguish them from errors in exception handling |
|
| B905 | zip-without-explicit-strict | zip() without an explicit strict= parameter |
For more, see flake8-builtins on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| A001 | builtin-variable-shadowing | Variable {name} is shadowing a python builtin |
|
| A002 | builtin-argument-shadowing | Argument {name} is shadowing a python builtin |
|
| A003 | builtin-attribute-shadowing | Class attribute {name} is shadowing a python builtin |
For more, see flake8-comprehensions on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| C400 | unnecessary-generator-list | Unnecessary generator (rewrite as a list comprehension) |
🛠 |
| C401 | unnecessary-generator-set | Unnecessary generator (rewrite as a set comprehension) |
🛠 |
| C402 | unnecessary-generator-dict | Unnecessary generator (rewrite as a dict comprehension) |
🛠 |
| C403 | unnecessary-list-comprehension-set | Unnecessary list comprehension (rewrite as a set comprehension) |
🛠 |
| C404 | unnecessary-list-comprehension-dict | Unnecessary list comprehension (rewrite as a dict comprehension) |
🛠 |
| C405 | unnecessary-literal-set | Unnecessary {obj_type} literal (rewrite as a set literal) |
🛠 |
| C406 | unnecessary-literal-dict | Unnecessary {obj_type} literal (rewrite as a dict literal) |
🛠 |
| C408 | unnecessary-collection-call | Unnecessary {obj_type} call (rewrite as a literal) |
🛠 |
| C409 | unnecessary-literal-within-tuple-call | Unnecessary {literal} literal passed to tuple() (rewrite as a tuple literal) |
🛠 |
| C410 | unnecessary-literal-within-list-call | Unnecessary {literal} literal passed to list() (remove the outer call to list()) |
🛠 |
| C411 | unnecessary-list-call | Unnecessary list call (remove the outer call to list()) |
🛠 |
| C413 | unnecessary-call-around-sorted | Unnecessary {func} call around sorted() |
🛠 |
| C414 | unnecessary-double-cast-or-process | Unnecessary {inner} call within {outer}() |
|
| C415 | unnecessary-subscript-reversal | Unnecessary subscript reversal of iterable within {func}() |
|
| C416 | unnecessary-comprehension | Unnecessary {obj_type} comprehension (rewrite using {obj_type}()) |
🛠 |
| C417 | unnecessary-map | Unnecessary map usage (rewrite using a generator expression) |
For more, see flake8-debugger on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| T100 | debugger | Trace found: {name} used |
For more, see flake8-errmsg on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| EM101 | raw-string-in-exception | Exception must not use a string literal, assign to variable first | |
| EM102 | f-string-in-exception | Exception must not use an f-string literal, assign to variable first | |
| EM103 | dot-format-in-exception | Exception must not use a .format() string directly, assign to variable first |
For more, see flake8-implicit-str-concat on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| ISC001 | single-line-implicit-string-concatenation | Implicitly concatenated string literals on one line | |
| ISC002 | multi-line-implicit-string-concatenation | Implicitly concatenated string literals over continuation line | |
| ISC003 | explicit-string-concatenation | Explicitly concatenated string should be implicitly concatenated |
For more, see flake8-import-conventions on GitHub.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICN001 | import-alias-is-not-conventional | {name} should be imported as {asname} |
For more, see flake8-print on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| T201 | print-found | print found |
🛠 |
| T203 | p-print-found | pprint found |
🛠 |
For more, see flake8-pytest-style on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PT001 | incorrect-fixture-parentheses-style | Use @pytest.fixture{expected_parens} over @pytest.fixture{actual_parens} |
🛠 |
| PT002 | fixture-positional-args | Configuration for fixture {function} specified via positional args, use kwargs |
|
| PT003 | extraneous-scope-function | scope='function' is implied in @pytest.fixture() |
|
| PT004 | missing-fixture-name-underscore | Fixture {function} does not return anything, add leading underscore |
|
| PT005 | incorrect-fixture-name-underscore | Fixture {function} returns a value, remove leading underscore |
|
| PT006 | parametrize-names-wrong-type | Wrong name(s) type in @pytest.mark.parametrize, expected {expected} |
🛠 |
| PT007 | parametrize-values-wrong-type | Wrong values type in @pytest.mark.parametrize expected {values} of {row} |
|
| PT008 | patch-with-lambda | Use return_value= instead of patching with lambda |
|
| PT009 | unittest-assertion | Use a regular assert instead of unittest-style {assertion} |
🛠 |
| PT010 | raises-without-exception | set the expected exception in pytest.raises() |
|
| PT011 | raises-too-broad | pytest.raises({exception}) is too broad, set the match parameter or use a more specific exception |
|
| PT012 | raises-with-multiple-statements | pytest.raises() block should contain a single simple statement |
|
| PT013 | incorrect-pytest-import | Found incorrect import of pytest, use simple import pytest instead |
|
| PT015 | assert-always-false | Assertion always fails, replace with pytest.fail() |
|
| PT016 | fail-without-message | No message passed to pytest.fail() |
|
| PT017 | assert-in-except | Found assertion on exception {name} in except block, use pytest.raises() instead |
|
| PT018 | composite-assertion | Assertion should be broken down into multiple parts | |
| PT019 | fixture-param-without-value | Fixture {name} without value is injected as parameter, use @pytest.mark.usefixtures instead |
|
| PT020 | deprecated-yield-fixture | @pytest.yield_fixture is deprecated, use @pytest.fixture |
|
| PT021 | fixture-finalizer-callback | Use yield instead of request.addfinalizer |
|
| PT022 | useless-yield-fixture | No teardown in fixture {name}, use return instead of yield |
🛠 |
| PT023 | incorrect-mark-parentheses-style | Use @pytest.mark.{mark_name}{expected_parens} over @pytest.mark.{mark_name}{actual_parens} |
🛠 |
| PT024 | unnecessary-asyncio-mark-on-fixture | pytest.mark.asyncio is unnecessary for fixtures |
🛠 |
| PT025 | erroneous-use-fixtures-on-fixture | pytest.mark.usefixtures has no effect on fixtures |
🛠 |
| PT026 | use-fixtures-without-parameters | Useless pytest.mark.usefixtures without parameters |
🛠 |
For more, see flake8-quotes on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q000 | bad-quotes-inline-string | Double quotes found but single quotes preferred | 🛠 |
| Q001 | bad-quotes-multiline-string | Double quote multiline found but single quotes preferred | 🛠 |
| Q002 | bad-quotes-docstring | Double quote docstring found but single quotes preferred | 🛠 |
| Q003 | avoid-quote-escape | Change outer quotes to avoid escaping inner quotes | 🛠 |
For more, see flake8-return on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| RET501 | unnecessary-return-none | Do not explicitly return None in function if it is the only possible return value |
🛠 |
| RET502 | implicit-return-value | Do not implicitly return None in function able to return non-None value |
🛠 |
| RET503 | implicit-return | Missing explicit return at the end of function able to return non-None value |
🛠 |
| RET504 | unnecessary-assign | Unnecessary variable assignment before return statement |
|
| RET505 | superfluous-else-return | Unnecessary {branch} after return statement |
|
| RET506 | superfluous-else-raise | Unnecessary {branch} after raise statement |
|
| RET507 | superfluous-else-continue | Unnecessary {branch} after continue statement |
|
| RET508 | superfluous-else-break | Unnecessary {branch} after break statement |
For more, see flake8-simplify on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| SIM101 | duplicate-isinstance-call | Multiple isinstance calls for {name}, merge into a single call |
🛠 |
| SIM102 | nested-if-statements | Use a single if statement instead of nested if statements |
🛠 |
| SIM103 | return-bool-condition-directly | Return the condition {cond} directly |
🛠 |
| SIM105 | use-contextlib-suppress | Use contextlib.suppress({exception}) instead of try-except-pass |
|
| SIM107 | return-in-try-except-finally | Don't use return in try/except and finally |
|
| SIM108 | use-ternary-operator | Use ternary operator {contents} instead of if-else-block |
🛠 |
| SIM109 | compare-with-tuple | Use {replacement} instead of multiple equality comparisons |
🛠 |
| SIM110 | convert-loop-to-any | Use {any} instead of for loop |
🛠 |
| SIM111 | convert-loop-to-all | Use {all} instead of for loop |
🛠 |
| SIM112 | use-capital-environment-variables | Use capitalized environment variable {expected} instead of {original} |
🛠 |
| SIM115 | open-file-with-context-handler | Use context handler for opening files | |
| SIM117 | multiple-with-statements | Use a single with statement with multiple contexts instead of nested with statements |
🛠 |
| SIM118 | key-in-dict | Use {key} in {dict} instead of {key} in {dict}.keys() |
🛠 |
| SIM201 | negate-equal-op | Use {left} != {right} instead of not {left} == {right} |
🛠 |
| SIM202 | negate-not-equal-op | Use {left} == {right} instead of not {left} != {right} |
🛠 |
| SIM208 | double-negation | Use {expr} instead of not (not {expr}) |
🛠 |
| SIM210 | if-expr-with-true-false | Use bool({expr}) instead of True if {expr} else False |
🛠 |
| SIM211 | if-expr-with-false-true | Use not {expr} instead of False if {expr} else True |
🛠 |
| SIM212 | if-expr-with-twisted-arms | Use {expr_else} if {expr_else} else {expr_body} instead of {expr_body} if not {expr_else} else {expr_else} |
🛠 |
| SIM220 | a-and-not-a | Use False instead of {name} and not {name} |
🛠 |
| SIM221 | a-or-not-a | Use True instead of {name} or not {name} |
🛠 |
| SIM222 | or-true | Use True instead of ... or True |
🛠 |
| SIM223 | and-false | Use False instead of ... and False |
🛠 |
| SIM300 | yoda-conditions | Yoda conditions are discouraged, use {suggestion} instead |
🛠 |
| SIM401 | dict-get-with-default | Use {contents} instead of an if block |
🛠 |
For more, see flake8-tidy-imports on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| TID251 | banned-api | {name} is banned: {message} |
|
| TID252 | relative-imports | Relative imports from parent modules are banned |
For more, see flake8-unused-arguments on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARG001 | unused-function-argument | Unused function argument: {name} |
|
| ARG002 | unused-method-argument | Unused method argument: {name} |
|
| ARG003 | unused-class-method-argument | Unused class method argument: {name} |
|
| ARG004 | unused-static-method-argument | Unused static method argument: {name} |
|
| ARG005 | unused-lambda-argument | Unused lambda argument: {name} |
For more, see flake8-datetimez on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| DTZ001 | call-datetime-without-tzinfo | The use of datetime.datetime() without tzinfo argument is not allowed |
|
| DTZ002 | call-datetime-today | The use of datetime.datetime.today() is not allowed |
|
| DTZ003 | call-datetime-utcnow | The use of datetime.datetime.utcnow() is not allowed |
|
| DTZ004 | call-datetime-utcfromtimestamp | The use of datetime.datetime.utcfromtimestamp() is not allowed |
|
| DTZ005 | call-datetime-now-without-tzinfo | The use of datetime.datetime.now() without tz argument is not allowed |
|
| DTZ006 | call-datetime-fromtimestamp | The use of datetime.datetime.fromtimestamp() without tz argument is not allowed |
|
| DTZ007 | call-datetime-strptime-without-zone | The use of datetime.datetime.strptime() without %z must be followed by .replace(tzinfo=) or .astimezone() |
|
| DTZ011 | call-date-today | The use of datetime.date.today() is not allowed. |
|
| DTZ012 | call-date-fromtimestamp | The use of datetime.date.fromtimestamp() is not allowed |
For more, see eradicate on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| ERA001 | commented-out-code | Found commented-out code | 🛠 |
For more, see pandas-vet on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PD002 | use-of-inplace-argument | inplace=True should be avoided; it has inconsistent behavior |
|
| PD003 | use-of-dot-is-null | .isna is preferred to .isnull; functionality is equivalent |
|
| PD004 | use-of-dot-not-null | .notna is preferred to .notnull; functionality is equivalent |
|
| PD007 | use-of-dot-ix | .ix is deprecated; use more explicit .loc or .iloc |
|
| PD008 | use-of-dot-at | Use .loc instead of .at. If speed is important, use numpy. |
|
| PD009 | use-of-dot-iat | Use .iloc instead of .iat. If speed is important, use numpy. |
|
| PD010 | use-of-dot-pivot-or-unstack | .pivot_table is preferred to .pivot or .unstack; provides same functionality |
|
| PD011 | use-of-dot-values | Use .to_numpy() instead of .values |
|
| PD012 | use-of-dot-read-table | .read_csv is preferred to .read_table; provides same functionality |
|
| PD013 | use-of-dot-stack | .melt is preferred to .stack; provides same functionality |
|
| PD015 | use-of-pd-merge | Use .merge method instead of pd.merge function. They have equivalent functionality. |
|
| PD901 | df-is-a-bad-variable-name | df is a bad variable name. Be kinder to your future self. |
For more, see pygrep-hooks on GitHub.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PGH001 | no-eval | No builtin eval() allowed |
|
| PGH002 | deprecated-log-warn | warn is deprecated in favor of warning |
|
| PGH003 | blanket-type-ignore | Use specific rule codes when ignoring type issues | |
| PGH004 | blanket-noqa | Use specific rule codes when using noqa |
For more, see Pylint on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLC0414 | useless-import-alias | Import alias does not rename original package | 🛠 |
| PLC3002 | unnecessary-direct-lambda-call | Lambda expression called directly. Execute the expression inline instead. |
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLE0117 | nonlocal-without-binding | Nonlocal name {name} found without binding |
|
| PLE0118 | used-prior-global-declaration | Name {name} is used prior to global declaration on line {line} |
|
| PLE1142 | await-outside-async | await should be used within an async function |
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLR0133 | constant-comparison | Two constants compared in a comparison, consider replacing {left_constant} {op} {right_constant} |
|
| PLR0206 | property-with-parameters | Cannot have defined parameters for properties | |
| PLR0402 | consider-using-from-import | Use from {module} import {name} in lieu of alias |
|
| PLR1701 | consider-merging-isinstance | Merge these isinstance calls: isinstance({obj}, ({types})) |
|
| PLR1722 | use-sys-exit | Use sys.exit() instead of {name} |
🛠 |
| PLR2004 | magic-value-comparison | Magic value used in comparison, consider replacing {value} with a constant variable |
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PLW0120 | useless-else-on-loop | Else clause on loop without a break statement, remove the else and de-indent all the code inside it | |
| PLW0602 | global-variable-not-assigned | Using global for {name} but no assignment is done |
For more, see flake8-pie on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PIE790 | no-unnecessary-pass | Unnecessary pass statement |
🛠 |
| PIE794 | dupe-class-field-definitions | Class field {name} is defined multiple times |
🛠 |
| PIE796 | prefer-unique-enums | Enum contains duplicate value: {value} |
|
| PIE800 | no-unnecessary-spread | Unnecessary spread ** |
|
| PIE804 | no-unnecessary-dict-kwargs | Unnecessary dict kwargs |
|
| PIE807 | prefer-list-builtin | Prefer list over useless lambda |
🛠 |
For more, see flake8-commas on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| COM812 | trailing-comma-missing | Trailing comma missing | 🛠 |
| COM818 | trailing-comma-on-bare-tuple-prohibited | Trailing comma on bare tuple prohibited | |
| COM819 | trailing-comma-prohibited | Trailing comma prohibited | 🛠 |
For more, see flake8-no-pep420 on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| INP001 | implicit-namespace-package | File {filename} is part of an implicit namespace package. Add an __init__.py. |
For more, see flake8-executable on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| EXE001 | shebang-not-executable | Shebang is present but file is not executable | |
| EXE002 | shebang-missing-executable-file | The file is executable but no shebang is present | |
| EXE003 | shebang-python | Shebang should contain "python" | |
| EXE004 | shebang-whitespace | Avoid whitespace before shebang | 🛠 |
| EXE005 | shebang-newline | Shebang should be at the beginning of the file |
For more, see flake8-type-checking on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| TCH001 | typing-only-first-party-import | Move application import {} into a type-checking block |
|
| TCH002 | typing-only-third-party-import | Move third-party import {} into a type-checking block |
|
| TCH003 | typing-only-standard-library-import | Move standard library import {} into a type-checking block |
|
| TCH004 | runtime-import-in-type-checking-block | Move import {} out of type-checking block. Import is used for more than type hinting. |
|
| TCH005 | empty-type-checking-block | Found empty type-checking block |
For more, see tryceratops on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRY002 | raise-vanilla-class | Create your own exception | |
| TRY003 | raise-vanilla-args | Avoid specifying long messages outside the exception class | |
| TRY004 | prefer-type-error | Prefer TypeError exception for invalid type |
🛠 |
| TRY200 | reraise-no-cause | Use raise from to specify exception cause |
|
| TRY201 | verbose-raise | Use raise without specifying exception name |
|
| TRY300 | try-consider-else | Consider else block |
|
| TRY301 | raise-within-try | Abstract raise to an inner function |
|
| TRY400 | error-instead-of-exception | Use logging.exception instead of logging.error |
For more, see flake8-use-pathlib on PyPI.
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTH100 | pathlib-abspath | os.path.abspath should be replaced by .resolve() |
|
| PTH101 | pathlib-chmod | os.chmod should be replaced by .chmod() |
|
| PTH102 | pathlib-mkdir | os.mkdir should be replaced by .mkdir() |
|
| PTH103 | pathlib-makedirs | os.makedirs should be replaced by .mkdir(parents=True) |
|
| PTH104 | pathlib-rename | os.rename should be replaced by .rename() |
|
| PTH105 | pathlib-replace | os.replaceshould be replaced by .replace() |
|
| PTH106 | pathlib-rmdir | os.rmdir should be replaced by .rmdir() |
|
| PTH107 | pathlib-remove | os.remove should be replaced by .unlink() |
|
| PTH108 | pathlib-unlink | os.unlink should be replaced by .unlink() |
|
| PTH109 | pathlib-getcwd | os.getcwd() should be replaced by Path.cwd() |
|
| PTH110 | pathlib-exists | os.path.exists should be replaced by .exists() |
|
| PTH111 | pathlib-expanduser | os.path.expanduser should be replaced by .expanduser() |
|
| PTH112 | pathlib-is-dir | os.path.isdir should be replaced by .is_dir() |
|
| PTH113 | pathlib-is-file | os.path.isfile should be replaced by .is_file() |
|
| PTH114 | pathlib-is-link | os.path.islink should be replaced by .is_symlink() |
|
| PTH115 | pathlib-readlink | os.readlink( should be replaced by .readlink() |
|
| PTH116 | pathlib-stat | os.stat should be replaced by .stat() or .owner() or .group() |
|
| PTH117 | pathlib-is-abs | os.path.isabs should be replaced by .is_absolute() |
|
| PTH118 | pathlib-join | os.path.join should be replaced by foo_path / "bar" |
|
| PTH119 | pathlib-basename | os.path.basename should be replaced by .name |
|
| PTH120 | pathlib-dirname | os.path.dirname should be replaced by .parent |
|
| PTH121 | pathlib-samefile | os.path.samefile should be replaced by .samefile() |
|
| PTH122 | pathlib-splitext | os.path.splitext should be replaced by .suffix |
|
| PTH123 | pathlib-open | open("foo") should be replaced byPath("foo").open() |
|
| PTH124 | pathlib-py-path | py.path is in maintenance mode, use pathlib instead |
| Code | Name | Message | Fix |
|---|---|---|---|
| RUF001 | ambiguous-unicode-character-string | String contains ambiguous unicode character '{confusable}' (did you mean '{representant}'?) | 🛠 |
| RUF002 | ambiguous-unicode-character-docstring | Docstring contains ambiguous unicode character '{confusable}' (did you mean '{representant}'?) | 🛠 |
| RUF003 | ambiguous-unicode-character-comment | Comment contains ambiguous unicode character '{confusable}' (did you mean '{representant}'?) | 🛠 |
| RUF004 | keyword-argument-before-star-argument | Keyword argument {name} must come after starred arguments |
|
| RUF005 | unpack-instead-of-concatenating-to-collection-literal | Consider {expr} instead of concatenation |
|
| RUF100 | unused-noqa | Unused blanket noqa directive |
🛠 |
Download the Ruff VS Code extension, which supports autofix actions, import sorting, and more.
Ruff supports the Language Server Protocol
via the ruff-lsp Python package, available on
PyPI.
ruff-lsp enables Ruff to be used with any editor that
supports the Language Server Protocol, including Neovim,
Sublime Text, Emacs, and more.
For example, to use ruff-lsp with Neovim, install ruff-lsp from PyPI along with
nvim-lspconfig. Then, add something like the following
to your init.lua:
-- See: https://github.com/neovim/nvim-lspconfig/tree/54eb2a070a4f389b1be0f98070f81d23e2b1a715#suggested-configuration
local opts = { noremap=true, silent=true }
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>e', vim.diagnostic.open_float, opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '[d', vim.diagnostic.goto_prev, opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', ']d', vim.diagnostic.goto_next, opts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>q', vim.diagnostic.setloclist, opts)
-- Use an on_attach function to only map the following keys
-- after the language server attaches to the current buffer
local on_attach = function(client, bufnr)
-- Enable completion triggered by <c-x><c-o>
vim.api.nvim_buf_set_option(bufnr, 'omnifunc', 'v:lua.vim.lsp.omnifunc')
-- Mappings.
-- See `:help vim.lsp.*` for documentation on any of the below functions
local bufopts = { noremap=true, silent=true, buffer=bufnr }
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gD', vim.lsp.buf.declaration, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gd', vim.lsp.buf.definition, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', 'K', vim.lsp.buf.hover, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gi', vim.lsp.buf.implementation, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<C-k>', vim.lsp.buf.signature_help, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>wa', vim.lsp.buf.add_workspace_folder, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>wr', vim.lsp.buf.remove_workspace_folder, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>wl', function()
print(vim.inspect(vim.lsp.buf.list_workspace_folders()))
end, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>D', vim.lsp.buf.type_definition, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>rn', vim.lsp.buf.rename, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>ca', vim.lsp.buf.code_action, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', 'gr', vim.lsp.buf.references, bufopts)
vim.keymap.set('n', '<space>f', function() vim.lsp.buf.format { async = true } end, bufopts)
end
-- Configure `ruff-lsp`.
local configs = require 'lspconfig.configs'
if not configs.ruff_lsp then
configs.ruff_lsp = {
default_config = {
cmd = { 'ruff-lsp' },
filetypes = { 'python' },
root_dir = require('lspconfig').util.find_git_ancestor,
init_options = {
settings = {
args = {}
}
}
}
}
end
require('lspconfig').ruff_lsp.setup {
on_attach = on_attach,
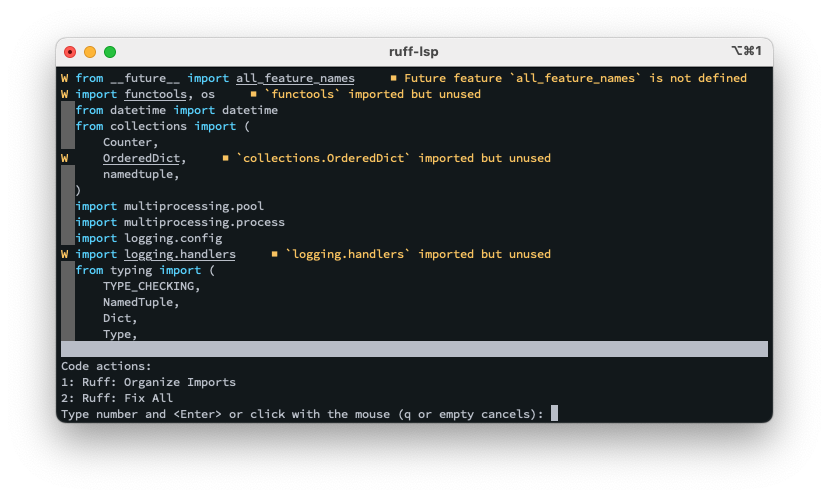
}Upon successful installation, you should see Ruff's diagnostics surfaced directly in your editor:
To use ruff-lsp with other editors, including Sublime Text and Helix, see the ruff-lsp documentation.
Ruff is also available as the python-lsp-ruff
plugin for python-lsp-server, both of which are
installable from PyPI:
pip install python-lsp-server python-lsp-ruffThe LSP server can then be used with any editor that supports the Language Server Protocol.
For example, to use python-lsp-ruff with Neovim, add something like the following to your
init.lua:
require'lspconfig'.pylsp.setup {
settings = {
pylsp = {
plugins = {
ruff = {
enabled = true
},
pycodestyle = {
enabled = false
},
pyflakes = {
enabled = false
},
mccabe = {
enabled = false
}
}
}
},
}Ruff can be integrated into any editor that supports the Language Server Protocol via ruff-lsp
(see: Language Server Protocol), including Vim and Neovim.
It's recommended that you use ruff-lsp, the
officially supported LSP server for Ruff.
However, Ruff is also available as part of the coc-pyright
extension for coc.nvim.
With the ALE plugin for (Neo)Vim.
let g:ale_linters = { "python": ["ruff"] }
let g:ale_fixers = {
\ "python": ["black", "ruff"],
\}Ruff can also be integrated via efm in just a few lines.
tools:
python-ruff: &python-ruff
lint-command: 'ruff --config ~/myconfigs/linters/ruff.toml --quiet ${INPUT}'
lint-stdin: true
lint-formats:
- '%f:%l:%c: %m'
format-command: 'ruff --stdin-filename ${INPUT} --config ~/myconfigs/linters/ruff.toml --fix --exit-zero --quiet -'
format-stdin: trueFor neovim users using null-ls, Ruff is already integrated.
local null_ls = require("null-ls")
local methods = require("null-ls.methods")
local helpers = require("null-ls.helpers")
local function ruff_fix()
return helpers.make_builtin({
name = "ruff",
meta = {
url = "https://github.com/charliermarsh/ruff/",
description = "An extremely fast Python linter, written in Rust.",
},
method = methods.internal.FORMATTING,
filetypes = { "python" },
generator_opts = {
command = "ruff",
args = { "--fix", "-e", "-n", "--stdin-filename", "$FILENAME", "-" },
to_stdin = true
},
factory = helpers.formatter_factory
})
end
null_ls.setup({
sources = {
ruff_fix(),
null_ls.builtins.diagnostics.ruff,
}
})Ruff can be installed as an External Tool in PyCharm. Open the Preferences pane, then navigate to "Tools", then "External Tools". From there, add a new tool with the following configuration:
Ruff should then appear as a runnable action:
Ruff is also available as the Ruff plugin on the IntelliJ Marketplace (maintained by @koxudaxi).
GitHub Actions has everything you need to run Ruff out-of-the-box:
name: CI
on: push
jobs:
build:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Install Python
uses: actions/setup-python@v4
with:
python-version: "3.11"
- name: Install dependencies
run: |
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
pip install ruff
# Include `--format=github` to enable automatic inline annotations.
- name: Run Ruff
run: ruff --format=github .Yes. Ruff is compatible with Black out-of-the-box, as long as
the line-length setting is consistent between the two.
As a project, Ruff is designed to be used alongside Black and, as such, will defer implementing stylistic lint rules that are obviated by autoformatting.
(Coming from Flake8? Try flake8-to-ruff to
automatically convert your existing configuration.)
Ruff can be used as a drop-in replacement for Flake8 when used (1) without or with a small number of plugins, (2) alongside Black, and (3) on Python 3 code.
Under those conditions, Ruff implements every rule in Flake8.
Ruff also re-implements some of the most popular Flake8 plugins and related code quality tools natively, including:
autoflake(#1647)eradicateflake8-2020flake8-annotationsflake8-bandit(#1646)flake8-blind-exceptflake8-boolean-trapflake8-bugbearflake8-builtinsflake8-commasflake8-comprehensionsflake8-datetimezflake8-debuggerflake8-docstringsflake8-eradicateflake8-errmsgflake8-executableflake8-implicit-str-concatflake8-import-conventionsflake8-no-pep420flake8-pie(#1543)flake8-printflake8-pytest-styleflake8-quotesflake8-returnflake8-simplify(#998)flake8-superflake8-tidy-importsisortmccabepandas-vetpep8-namingpydocstylepygrep-hooks(#980)pyupgrade(#827)yesqa
Note that, in some cases, Ruff uses different rule codes and prefixes than would be found in the
originating Flake8 plugins. For example, Ruff uses TID252 to represent the I252 rule from
flake8-tidy-imports. This helps minimize conflicts across plugins and allows any individual plugin
to be toggled on or off with a single (e.g.) --select TID, as opposed to --select I2 (to avoid
conflicts with the isort rules, like I001).
Beyond the rule set, Ruff suffers from the following limitations vis-à-vis Flake8:
- Ruff does not yet support structural pattern matching.
- Flake8 has a plugin architecture and supports writing custom lint rules. (Instead, popular Flake8 plugins are re-implemented in Rust as part of Ruff itself.)
There are a few other minor incompatibilities between Ruff and the originating Flake8 plugins:
- Ruff doesn't implement all the "opinionated" lint rules from
flake8-bugbear. - Depending on your project structure, Ruff and
isortcan differ in their detection of first-party code. (This is often solved by modifying thesrcproperty, e.g., tosrc = ["src"], if your code is nested in asrcdirectory.)
At time of writing, Pylint implements 409 total rules, while Ruff implements 224, of which at least 60 overlap with the Pylint rule set. Subjectively, Pylint tends to implement more rules based on type inference (e.g., validating the number of arguments in a function call).
Like Flake8, Pylint supports plugins (called "checkers"), while Ruff implements all rules natively.
Unlike Pylint, Ruff is capable of automatically fixing its own lint violations.
Pylint parity is being tracked in #970.
Today, Ruff can be used to replace Flake8 when used with any of the following plugins:
flake8-2020flake8-annotationsflake8-bandit(#1646)flake8-blind-exceptflake8-boolean-trapflake8-bugbearflake8-builtinsflake8-commasflake8-comprehensionsflake8-datetimezflake8-debuggerflake8-docstringsflake8-eradicateflake8-errmsgflake8-executableflake8-implicit-str-concatflake8-import-conventionsflake8-no-pep420flake8-pie(#1543)flake8-printflake8-pytest-styleflake8-quotesflake8-returnflake8-simplify(#998)flake8-superflake8-tidy-importsmccabepandas-vetpep8-namingpydocstyle
Ruff can also replace isort,
yesqa, eradicate,
pygrep-hooks (#980), and a subset of the rules
implemented in pyupgrade (#827).
If you're looking to use Ruff, but rely on an unsupported Flake8 plugin, feel free to file an Issue.
Nope! Ruff is available as ruff on PyPI:
pip install ruffRuff ships with wheels for all major platforms, which enables pip to install Ruff without relying
on Rust at all.
Ruff does not yet support third-party plugins, though a plugin system is within-scope for the project. See #283 for more.
How does Ruff's import sorting compare to isort?
Ruff's import sorting is intended to be nearly equivalent to isort when used profile = "black".
There are a few known, minor differences in how Ruff and isort break ties between similar imports,
and in how Ruff and isort treat inline comments in some cases (see: #1381,
#2104).
Like isort, Ruff's import sorting is compatible with Black.
Ruff does not yet support all of isort's configuration options, though it does support many of
them. You can find the supported settings in the API reference. For example, you can set
known-first-party like so:
[tool.ruff]
select = [
# Pyflakes
"F",
# Pycodestyle
"E",
"W",
# isort
"I001"
]
src = ["src", "tests"]
[tool.ruff.isort]
known-first-party = ["my_module1", "my_module2"]Ruff is integrated into nbQA, a tool for running linters and code formatters over Jupyter Notebooks.
After installing ruff and nbqa, you can run Ruff over a notebook like so:
> nbqa ruff Untitled.ipynb
Untitled.ipynb:cell_1:2:5: F841 Local variable `x` is assigned to but never used
Untitled.ipynb:cell_2:1:1: E402 Module level import not at top of file
Untitled.ipynb:cell_2:1:8: F401 `os` imported but unused
Found 3 errors.
1 potentially fixable with the --fix option.Yes! To enable specific docstring convention, add the following to your pyproject.toml:
[tool.ruff.pydocstyle]
convention = "google" # Accepts: "google", "numpy", or "pep257".For example, if you're coming from flake8-docstrings, and your originating configuration uses
--docstring-convention=numpy, you'd instead set convention = "numpy" in your pyproject.toml,
as above.
Alongside convention, you'll want to explicitly enable the D rule code prefix, like so:
[tool.ruff]
select = [
"D",
]
[tool.ruff.pydocstyle]
convention = "google"Setting a convention force-disables any rules that are incompatible with that convention, no
matter how they're provided, which avoids accidental incompatibilities and simplifies configuration.
Run ruff /path/to/code.py --show-settings to view the resolved settings for a given file.
Ruff's autofix is a best-effort mechanism. Given the dynamic nature of Python, it's difficult to have complete certainty when making changes to code, even for the seemingly trivial fixes.
In the future, Ruff will support enabling autofix behavior based on the safety of the patch.
In the meantime, if you find that the autofix is too aggressive, you can disable it on a per-rule or
per-category basis using the unfixable mechanic. For example, to disable autofix
for some possibly-unsafe rules, you could add the following to your pyproject.toml:
[tool.ruff]
unfixable = ["B", "SIM", "TRY", "RUF"]If you find a case where Ruff's autofix breaks your code, please file an Issue!
Contributions are welcome and hugely appreciated. To get started, check out the contributing guidelines.
Ruff is distributed on PyPI, and published via maturin.
See: .github/workflows/release.yaml.
First, clone CPython. It's a large and diverse Python codebase, which makes it a good target for benchmarking.
git clone --branch 3.10 https://github.com/python/cpython.git resources/test/cpythonTo benchmark the release build:
cargo build --release && hyperfine --ignore-failure --warmup 10 \
"./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/ --no-cache" \
"./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/"
Benchmark 1: ./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/ --no-cache
Time (mean ± σ): 293.8 ms ± 3.2 ms [User: 2384.6 ms, System: 90.3 ms]
Range (min … max): 289.9 ms … 301.6 ms 10 runs
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
Benchmark 2: ./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/
Time (mean ± σ): 48.0 ms ± 3.1 ms [User: 65.2 ms, System: 124.7 ms]
Range (min … max): 45.0 ms … 66.7 ms 62 runs
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
Summary
'./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/' ran
6.12 ± 0.41 times faster than './target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/ --no-cache'To benchmark against the ecosystem's existing tools:
hyperfine --ignore-failure --warmup 5 \
"./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/ --no-cache" \
"pyflakes resources/test/cpython" \
"autoflake --recursive --expand-star-imports --remove-all-unused-imports --remove-unused-variables --remove-duplicate-keys resources/test/cpython" \
"pycodestyle resources/test/cpython" \
"flake8 resources/test/cpython"
Benchmark 1: ./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/ --no-cache
Time (mean ± σ): 294.3 ms ± 3.3 ms [User: 2467.5 ms, System: 89.6 ms]
Range (min … max): 291.1 ms … 302.8 ms 10 runs
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
Benchmark 2: pyflakes resources/test/cpython
Time (mean ± σ): 15.786 s ± 0.143 s [User: 15.560 s, System: 0.214 s]
Range (min … max): 15.640 s … 16.157 s 10 runs
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
Benchmark 3: autoflake --recursive --expand-star-imports --remove-all-unused-imports --remove-unused-variables --remove-duplicate-keys resources/test/cpython
Time (mean ± σ): 6.175 s ± 0.169 s [User: 54.102 s, System: 1.057 s]
Range (min … max): 5.950 s … 6.391 s 10 runs
Benchmark 4: pycodestyle resources/test/cpython
Time (mean ± σ): 46.921 s ± 0.508 s [User: 46.699 s, System: 0.202 s]
Range (min … max): 46.171 s … 47.863 s 10 runs
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
Benchmark 5: flake8 resources/test/cpython
Time (mean ± σ): 12.260 s ± 0.321 s [User: 102.934 s, System: 1.230 s]
Range (min … max): 11.848 s … 12.933 s 10 runs
Warning: Ignoring non-zero exit code.
Summary
'./target/release/ruff ./resources/test/cpython/ --no-cache' ran
20.98 ± 0.62 times faster than 'autoflake --recursive --expand-star-imports --remove-all-unused-imports --remove-unused-variables --remove-duplicate-keys resources/test/cpython'
41.66 ± 1.18 times faster than 'flake8 resources/test/cpython'
53.64 ± 0.77 times faster than 'pyflakes resources/test/cpython'
159.43 ± 2.48 times faster than 'pycodestyle resources/test/cpython'You can run poetry install from ./scripts to create a working environment for the above. All
reported benchmarks were computed using the versions specified by ./scripts/pyproject.toml
on Python 3.11.
To benchmark Pylint, remove the following files from the CPython repository:
rm Lib/test/bad_coding.py \
Lib/test/bad_coding2.py \
Lib/test/bad_getattr.py \
Lib/test/bad_getattr2.py \
Lib/test/bad_getattr3.py \
Lib/test/badcert.pem \
Lib/test/badkey.pem \
Lib/test/badsyntax_3131.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future10.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future3.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future4.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future5.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future6.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future7.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future8.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_future9.py \
Lib/test/badsyntax_pep3120.py \
Lib/test/test_asyncio/test_runners.py \
Lib/test/test_copy.py \
Lib/test/test_inspect.py \
Lib/test/test_typing.pyThen, from resources/test/cpython, run: time pylint -j 0 -E $(git ls-files '*.py'). This
will execute Pylint with maximum parallelism and only report errors.
To benchmark Pyupgrade, run the following from resources/test/cpython:
hyperfine --ignore-failure --warmup 5 --prepare "git reset --hard HEAD" \
"find . -type f -name \"*.py\" | xargs -P 0 pyupgrade --py311-plus"
Benchmark 1: find . -type f -name "*.py" | xargs -P 0 pyupgrade --py311-plus
Time (mean ± σ): 30.119 s ± 0.195 s [User: 28.638 s, System: 0.390 s]
Range (min … max): 29.813 s … 30.356 s 10 runsA list of allowed "confusable" Unicode characters to ignore when
enforcing RUF001, RUF002, and RUF003.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<char>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Allow minus-sign (U+2212), greek-small-letter-rho (U+03C1), and the asterisk-operator (U+2217),
# which could be confused for "-", "p", and "*", respectively.
allowed-confusables = ["−", "ρ", "∗"]A list of builtins to treat as defined references, in addition to the system builtins.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
builtins = ["_"]A path to the cache directory.
By default, Ruff stores cache results in a .ruff_cache directory in
the current project root.
However, Ruff will also respect the RUFF_CACHE_DIR environment
variable, which takes precedence over that default.
This setting will override even the RUFF_CACHE_DIR environment
variable, if set.
Default value: .ruff_cache
Type: PathBuf
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
cache-dir = "~/.cache/ruff"A regular expression used to identify "dummy" variables, or those which
should be ignored when enforcing (e.g.) unused-variable rules. The
default expression matches _, __, and _var, but not _var_.
Default value: "^(_+|(_+[a-zA-Z0-9_]*[a-zA-Z0-9]+?))$"
Type: Regex
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Only ignore variables named "_".
dummy-variable-rgx = "^_$"A list of file patterns to exclude from linting.
Exclusions are based on globs, and can be either:
- Single-path patterns, like
.mypy_cache(to exclude any directory named.mypy_cachein the tree),foo.py(to exclude any file namedfoo.py), orfoo_*.py(to exclude any file matchingfoo_*.py). - Relative patterns, like
directory/foo.py(to exclude that specific file) ordirectory/*.py(to exclude any Python files indirectory). Note that these paths are relative to the project root (e.g., the directory containing yourpyproject.toml).
For more information on the glob syntax, refer to the globset documentation.
Note that you'll typically want to use
extend-exclude to modify the excluded paths.
Default value: [".bzr", ".direnv", ".eggs", ".git", ".hg", ".mypy_cache", ".nox", ".pants.d", ".ruff_cache", ".svn", ".tox", ".venv", "__pypackages__", "_build", "buck-out", "build", "dist", "node_modules", "venv"]
Type: Vec<FilePattern>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
exclude = [".venv"]A path to a local pyproject.toml file to merge into this
configuration. User home directory and environment variables will be
expanded.
To resolve the current pyproject.toml file, Ruff will first resolve
this base configuration file, then merge in any properties defined
in the current configuration file.
Default value: None
Type: Path
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Extend the `pyproject.toml` file in the parent directory.
extend = "../pyproject.toml"
# But use a different line length.
line-length = 100A list of file patterns to omit from linting, in addition to those
specified by exclude.
Exclusions are based on globs, and can be either:
- Single-path patterns, like
.mypy_cache(to exclude any directory named.mypy_cachein the tree),foo.py(to exclude any file namedfoo.py), orfoo_*.py(to exclude any file matchingfoo_*.py). - Relative patterns, like
directory/foo.py(to exclude that specific file) ordirectory/*.py(to exclude any Python files indirectory). Note that these paths are relative to the project root (e.g., the directory containing yourpyproject.toml).
For more information on the glob syntax, refer to the globset documentation.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<FilePattern>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# In addition to the standard set of exclusions, omit all tests, plus a specific file.
extend-exclude = ["tests", "src/bad.py"]A list of rule codes or prefixes to ignore, in addition to those
specified by ignore.
Note that extend-ignore is applied after resolving rules from
ignore/select and a less specific rule in extend-ignore
would overwrite a more specific rule in select. It is
recommended to only use extend-ignore when extending a
pyproject.toml file via extend.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<RuleSelector>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Skip unused variable rules (`F841`).
extend-ignore = ["F841"]A list of rule codes or prefixes to enable, in addition to those
specified by select.
Note that extend-select is applied after resolving rules from
ignore/select and a less specific rule in extend-select
would overwrite a more specific rule in ignore. It is
recommended to only use extend-select when extending a
pyproject.toml file via extend.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<RuleSelector>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# On top of the default `select` (`E`, `F`), enable flake8-bugbear (`B`) and flake8-quotes (`Q`).
extend-select = ["B", "Q"]A list of rule codes that are unsupported by Ruff, but should be
preserved when (e.g.) validating # noqa directives. Useful for
retaining # noqa directives that cover plugins not yet implemented
by Ruff.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Avoiding flagging (and removing) `V101` from any `# noqa`
# directives, despite Ruff's lack of support for `vulture`.
external = ["V101"]Enable autofix behavior by-default when running ruff (overridden
by the --fix and --no-fix command-line flags).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
fix = trueLike fix, but disables reporting on leftover violation. Implies fix.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
fix-only = trueA list of rule codes or prefixes to consider autofixable.
Default value: ["A", "ANN", "ARG", "B", "BLE", "C", "D", "E", "ERA", "F", "FBT", "I", "ICN", "N", "PGH", "PLC", "PLE", "PLR", "PLW", "Q", "RET", "RUF", "S", "T", "TID", "UP", "W", "YTT"]
Type: Vec<RuleSelector>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Only allow autofix behavior for `E` and `F` rules.
fixable = ["E", "F"]Whether to enforce exclude and extend-exclude patterns, even for
paths that are passed to Ruff explicitly. Typically, Ruff will lint
any paths passed in directly, even if they would typically be
excluded. Setting force-exclude = true will cause Ruff to
respect these exclusions unequivocally.
This is useful for pre-commit, which explicitly passes all
changed files to the ruff-pre-commit
plugin, regardless of whether they're marked as excluded by Ruff's own
settings.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
force-exclude = trueThe style in which violation messages should be formatted: "text"
(default), "grouped" (group messages by file), "json"
(machine-readable), "junit" (machine-readable XML), "github" (GitHub
Actions annotations), "gitlab" (GitLab CI code quality report), or
"pylint" (Pylint text format).
Default value: "text"
Type: SerializationType
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Group violations by containing file.
format = "grouped"A list of rule codes or prefixes to ignore. Prefixes can specify exact
rules (like F841), entire categories (like F), or anything in
between.
When breaking ties between enabled and disabled rules (via select and
ignore, respectively), more specific prefixes override less
specific prefixes.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<RuleSelector>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Skip unused variable rules (`F841`).
ignore = ["F841"]Avoid automatically removing unused imports in __init__.py files. Such
imports will still be flagged, but with a dedicated message suggesting
that the import is either added to the module's __all__ symbol, or
re-exported with a redundant alias (e.g., import os as os).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
ignore-init-module-imports = trueThe line length to use when enforcing long-lines violations (like
E501).
Default value: 88
Type: usize
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Allow lines to be as long as 120 characters.
line-length = 120Mark the specified directories as namespace packages. For the purpose of
module resolution, Ruff will treat those directories as if they
contained an __init__.py file.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<PathBuf>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
namespace-packages = ["airflow/providers"]A list of mappings from file pattern to rule codes or prefixes to exclude, when considering any matching files.
Default value: {}
Type: HashMap<String, Vec<RuleSelector>>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Ignore `E402` (import violations) in all `__init__.py` files, and in `path/to/file.py`.
[tool.ruff.per-file-ignores]
"__init__.py" = ["E402"]
"path/to/file.py" = ["E402"]Require a specific version of Ruff to be running (useful for unifying
results across many environments, e.g., with a pyproject.toml
file).
Default value: None
Type: String
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
required-version = "0.0.193"Whether to automatically exclude files that are ignored by .ignore,
.gitignore, .git/info/exclude, and global gitignore files.
Enabled by default.
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
respect-gitignore = falseA list of rule codes or prefixes to enable. Prefixes can specify exact
rules (like F841), entire categories (like F), or anything in
between.
When breaking ties between enabled and disabled rules (via select and
ignore, respectively), more specific prefixes override less
specific prefixes.
Default value: ["E", "F"]
Type: Vec<RuleSelector>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# On top of the defaults (`E`, `F`), enable flake8-bugbear (`B`) and flake8-quotes (`Q`).
select = ["E", "F", "B", "Q"]Whether to show source code snippets when reporting lint violations
(overridden by the --show-source command-line flag).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# By default, always show source code snippets.
show-source = trueThe source code paths to consider, e.g., when resolving first- vs. third-party imports.
As an example: given a Python package structure like:
my_package/
pyproject.toml
src/
my_package/
__init__.py
foo.py
bar.py
The src directory should be included in source (e.g., source = ["src"]), such that when resolving imports, my_package.foo is
considered a first-party import.
This field supports globs. For example, if you have a series of Python
packages in a python_modules directory, src = ["python_modules/*"] would expand to incorporate all of the
packages in that directory. User home directory and environment
variables will also be expanded.
Default value: ["."]
Type: Vec<PathBuf>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Allow imports relative to the "src" and "test" directories.
src = ["src", "test"]The Python version to target, e.g., when considering automatic code upgrades, like rewriting type annotations. Note that the target version will not be inferred from the current Python version, and instead must be specified explicitly (as seen below).
Default value: "py310"
Type: PythonVersion
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Always generate Python 3.7-compatible code.
target-version = "py37"A list of task tags to recognize (e.g., "TODO", "FIXME", "XXX").
Comments starting with these tags will be ignored by commented-out code
detection (ERA), and skipped by line-length rules (E501) if
ignore-overlong-task-comments is set to true.
Default value: ["TODO", "FIXME", "XXX"]
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
task-tags = ["HACK"]A list of modules whose imports should be treated equivalently to
members of the typing module.
This is useful for ensuring proper type annotation inference for
projects that re-export typing and typing_extensions members
from a compatibility module. If omitted, any members imported from
modules apart from typing and typing_extensions will be treated
as ordinary Python objects.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
typing-modules = ["airflow.typing_compat"]A list of rule codes or prefixes to consider non-autofix-able.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<RuleSelector>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
# Disable autofix for unused imports (`F401`).
unfixable = ["F401"]Enable or disable automatic update checks (overridden by the
--update-check and --no-update-check command-line flags).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff]
update-check = trueWhether to suppress ANN401 for dynamically typed *args and
**kwargs arguments.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-annotations]
allow-star-arg-any = trueWhether to allow the omission of a return type hint for __init__ if at
least one argument is annotated.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-annotations]
mypy-init-return = trueWhether to suppress ANN000-level violations for arguments matching the
"dummy" variable regex (like _).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-annotations]
suppress-dummy-args = trueWhether to suppress ANN200-level violations for functions that meet
either of the following criteria:
- Contain no
returnstatement. - Explicit
returnstatement(s) all returnNone(explicitly or implicitly).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-annotations]
suppress-none-returning = trueA list of directories to consider temporary.
Default value: ["/tmp", "/var/tmp", "/dev/shm"]
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-bandit]
hardcoded-tmp-directory = ["/foo/bar"]A list of directories to consider temporary, in addition to those
specified by hardcoded-tmp-directory.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-bandit]
extend-hardcoded-tmp-directory = ["/foo/bar"]Additional callable functions to consider "immutable" when evaluating,
e.g., the no-mutable-default-argument rule (B006).
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-bugbear]
# Allow default arguments like, e.g., `data: List[str] = fastapi.Query(None)`.
extend-immutable-calls = ["fastapi.Depends", "fastapi.Query"]Ignore list of builtins.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-builtins]
builtins-ignorelist = ["id"]Maximum string length for string literals in exception messages.
Default value: 0
Type: usize
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-errmsg]
max-string-length = 20Whether to allow implicit string concatenations for multiline strings. By default, implicit concatenations of multiline strings are allowed (but continuation lines, delimited with a backslash, are prohibited).
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-implicit-str-concat]
allow-multiline = falseThe conventional aliases for imports. These aliases can be extended by
the extend_aliases option.
Default value: {"altair": "alt", "matplotlib.pyplot": "plt", "numpy": "np", "pandas": "pd", "seaborn": "sns"}
Type: FxHashMap<String, String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-import-conventions]
[tool.ruff.flake8-import-conventions.aliases]
# Declare the default aliases.
altair = "alt"
"matplotlib.pyplot" = "plt"
numpy = "np"
pandas = "pd"
seaborn = "sns"A mapping of modules to their conventional import aliases. These aliases
will be added to the aliases mapping.
Default value: {}
Type: FxHashMap<String, String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-import-conventions]
[tool.ruff.flake8-import-conventions.extend-aliases]
# Declare a custom alias for the `matplotlib` module.
"dask.dataframe" = "dd"Boolean flag specifying whether @pytest.fixture() without parameters
should have parentheses. If the option is set to true (the
default), @pytest.fixture() is valid and @pytest.fixture is
invalid. If set to false, @pytest.fixture is valid and
@pytest.fixture() is invalid.
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
fixture-parentheses = trueBoolean flag specifying whether @pytest.mark.foo() without parameters
should have parentheses. If the option is set to true (the
default), @pytest.mark.foo() is valid and @pytest.mark.foo is
invalid. If set to false, @pytest.fixture is valid and
@pytest.mark.foo() is invalid.
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
mark-parentheses = trueExpected type for multiple argument names in @pytest.mark.parametrize.
The following values are supported:
csv— a comma-separated list, e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize('name1,name2', ...)tuple(default) — e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize(('name1', 'name2'), ...)list— e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize(['name1', 'name2'], ...)
Default value: tuple
Type: ParametrizeNameType
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
parametrize-names-type = "list"Expected type for each row of values in @pytest.mark.parametrize in
case of multiple parameters. The following values are supported:
tuple(default) — e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize(('name1', 'name2'), [(1, 2), (3, 4)])list— e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize(('name1', 'name2'), [[1, 2], [3, 4]])
Default value: tuple
Type: ParametrizeValuesRowType
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
parametrize-values-row-type = "list"Expected type for the list of values rows in @pytest.mark.parametrize.
The following values are supported:
tuple— e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize('name', (1, 2, 3))list(default) — e.g.@pytest.mark.parametrize('name', [1, 2, 3])
Default value: list
Type: ParametrizeValuesType
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
parametrize-values-type = "tuple"List of additional exception names that require a match= parameter in a
pytest.raises() call. This extends the default list of exceptions
that require a match= parameter.
This option is useful if you want to extend the default list of
exceptions that require a match= parameter without having to specify
the entire list.
Note that this option does not remove any exceptions from the default
list.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
raises-extend-require-match-for = ["requests.RequestException"]List of exception names that require a match= parameter in a
pytest.raises() call.
Default value: ["BaseException", "Exception", "ValueError", "OSError", "IOError", "EnvironmentError", "socket.error"]
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-pytest-style]
raises-require-match-for = ["requests.RequestException"]Whether to avoid using single quotes if a string contains single quotes, or vice-versa with double quotes, as per PEP8. This minimizes the need to escape quotation marks within strings.
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-quotes]
# Don't bother trying to avoid escapes.
avoid-escape = falseQuote style to prefer for docstrings (either "single" (') or "double"
(")).
Default value: "double"
Type: Quote
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-quotes]
docstring-quotes = "single"Quote style to prefer for inline strings (either "single" (') or
"double" (")).
Default value: "double"
Type: Quote
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-quotes]
inline-quotes = "single"Quote style to prefer for multiline strings (either "single" (') or
"double" (")).
Default value: "double"
Type: Quote
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-quotes]
multiline-quotes = "single"Whether to ban all relative imports ("all"), or only those imports
that extend into the parent module or beyond ("parents").
Default value: "parents"
Type: Strictness
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-tidy-imports]
# Disallow all relative imports.
ban-relative-imports = "all"Specific modules or module members that may not be imported or accessed.
Note that this rule is only meant to flag accidental uses,
and can be circumvented via eval or importlib.
Default value: {}
Type: HashMap<String, BannedApi>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-tidy-imports]
[tool.ruff.flake8-tidy-imports.banned-api]
"cgi".msg = "The cgi module is deprecated, see https://peps.python.org/pep-0594/#cgi."
"typing.TypedDict".msg = "Use typing_extensions.TypedDict instead."Whether to allow unused variadic arguments, like *args and **kwargs.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.flake8-unused-arguments]
ignore-variadic-names = trueAn override list of tokens to always recognize as a Class for
order-by-type regardless of casing.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
classes = ["SVC"]Combines as imports on the same line. See isort's combine-as-imports
option.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
combine-as-imports = trueAn override list of tokens to always recognize as a CONSTANT
for order-by-type regardless of casing.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
constants = ["constant"]A list of modules to consider standard-library, in addition to those known to Ruff in advance.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
extra-standard-library = ["path"]Forces all from imports to appear on their own line.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
force-single-line = trueDon't sort straight-style imports (like import sys) before from-style
imports (like from itertools import groupby). Instead, sort the
imports by module, independent of import style.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
force-sort-within-sections = trueForce import from statements with multiple members and at least one
alias (e.g., import A as B) to wrap such that every line contains
exactly one member. For example, this formatting would be retained,
rather than condensing to a single line:
from .utils import (
test_directory as test_directory,
test_id as test_id
)Note that this setting is only effective when combined with
combine-as-imports = true. When combine-as-imports isn't
enabled, every aliased import from will be given its own line, in
which case, wrapping is not necessary.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
force-wrap-aliases = true
combine-as-imports = trueA list of modules to consider first-party, regardless of whether they can be identified as such via introspection of the local filesystem.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
known-first-party = ["src"]A list of modules to consider third-party, regardless of whether they can be identified as such via introspection of the local filesystem.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
known-third-party = ["src"]A list of sections that should not be delineated from the previous section via empty lines.
Default value: []
Type: Option<Vec<ImportType>>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
no-lines-before = ["future", "standard-library"]Order imports by type, which is determined by case, in addition to alphabetically.
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
order-by-type = trueWhether to place "closer" imports (fewer . characters, most local)
before "further" imports (more . characters, least local), or vice
versa.
The default ("furthest-to-closest") is equivalent to isort's
reverse-relative default (reverse-relative = false); setting
this to "closest-to-furthest" is equivalent to isort's reverse-relative = true.
Default value: furthest-to-closest
Type: RelatveImportsOrder
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
relative-imports-order = "closest-to-furthest"Add the specified import line to all files.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
required-imports = ["from __future__ import annotations"]One or more modules to exclude from the single line rule.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
single-line-exclusions = ["os", "json"]If a comma is placed after the last member in a multi-line import, then the imports will never be folded into one line.
See isort's split-on-trailing-comma option.
Default value: true
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
split-on-trailing-comma = falseAn override list of tokens to always recognize as a var
for order-by-type regardless of casing.
Default value: []
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.isort]
variables = ["VAR"]The maximum McCabe complexity to allow before triggering C901 errors.
Default value: 10
Type: usize
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.mccabe]
# Flag errors (`C901`) whenever the complexity level exceeds 5.
max-complexity = 5A list of decorators that, when applied to a method, indicate that the
method should be treated as a class method. For example, Ruff will
expect that any method decorated by a decorator in this list takes a
cls argument as its first argument.
Default value: ["classmethod"]
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pep8-naming]
# Allow Pydantic's `@validator` decorator to trigger class method treatment.
classmethod-decorators = ["classmethod", "pydantic.validator"]A list of names to ignore when considering pep8-naming violations.
Default value: ["setUp", "tearDown", "setUpClass", "tearDownClass", "setUpModule", "tearDownModule", "asyncSetUp", "asyncTearDown", "setUpTestData", "failureException", "longMessage", "maxDiff"]
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pep8-naming]
ignore-names = ["callMethod"]A list of decorators that, when applied to a method, indicate that the
method should be treated as a static method. For example, Ruff will
expect that any method decorated by a decorator in this list has no
self or cls argument.
Default value: ["staticmethod"]
Type: Vec<String>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pep8-naming]
# Allow a shorthand alias, `@stcmthd`, to trigger static method treatment.
staticmethod-decorators = ["staticmethod", "stcmthd"]Whether or not line-length violations (E501) should be triggered for
comments starting with task-tags (by default: ["TODO", "FIXME",
and "XXX"]).
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pycodestyle]
ignore-overlong-task-comments = trueThe maximum line length to allow for line-length violations within
documentation (W505), including standalone comments.
Default value: None
Type: usize
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pycodestyle]
max-doc-length = 88Whether to use Google-style or NumPy-style conventions or the PEP257 defaults when analyzing docstring sections.
Default value: None
Type: Convention
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pydocstyle]
# Use Google-style docstrings.
convention = "google"Constant types to ignore when used as "magic values".
Default value: ["str"]
Type: Vec<ConstantType>
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pylint]
allow-magic-value-types = ["int"]Whether to avoid PEP 585 (List[int] -> list[int]) and PEP 604
(Optional[str] -> str | None) rewrites even if a file imports from __future__ import annotations. Note that this setting is only
applicable when the target Python version is below 3.9 and 3.10
respectively.
Default value: false
Type: bool
Example usage:
[tool.ruff.pyupgrade]
# Preserve types, even if a file imports `from __future__ import annotations`.
keep-runtime-typing = trueMIT